JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI
Journal of Health and Nutrition ResearchJournal of Health and Nutrition ResearchHemodialysis patients self-management is critical for maintaining their quality of life and minimizing complications. Patients health literacy and perception of the disease are essential for their acceptance of the condition and treatment. However, the relationship between these variables and self-management among hemodialysis patients remains unclear. This study aims to identify the relationship between health literacy, perception of disease, and self-management among hemodialysis patients. This correlational study was cross-sectional design, with 129 hemodialysis patients consecutively recruited from a hemodialysis unit of a tertiary hospital in West Java, Indonesia. Data were collected using the Brief-Illness Perception Questionnaire (Brief-IPQ), the European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire (HLS-EU-Q47), and the End Stage Renal Disease Adherence Questionnaire (ESRD-AQ). The data were analyzed using Pearson correlation analysis. Most of the patients had sufficient or excellent health literacy (74.4%), negative illness perception (50.4%), and low self-management practices (71.3%). Pearsons correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation was found between health literacy and self-management practices (r = .189; ρ=0.032). Additionally, there was a negative correlation between illness perception and health literacy (r = -.27; ρ= .002) as well as between illness perception and self-management practices (r = -.762; ρ= .000). Positive illness perception and better self-management practices correlate with a higher level of health literacy. These findings highlight the importance for healthcare staff to facilitate positive illness perceptions and self-management practices, and to consider these factors as vital aspects in developing self-management education programs for ESRD patients.
Hemodialysis patients must engage in self-management for effective treatment.This study describes higher health literacy and more positive illness perception correlating with better self-management.Non-adherence with self-management can lead to deteriorating conditions and decreased quality of life.Healthcare workers should provide interventions to enhance health literacy and patient perceptions of disease, thereby improving adherence to self-management.
Berdasarkan temuan penelitian ini, beberapa saran penelitian lanjutan dapat dipertimbangkan. Pertama, penelitian lebih lanjut perlu dilakukan untuk menguji efektivitas intervensi yang dirancang khusus untuk meningkatkan literasi kesehatan pasien hemodialisis, dengan fokus pada penyampaian informasi yang mudah dipahami dan relevan dengan kebutuhan sehari-hari mereka. Kedua, studi kualitatif dapat dilakukan untuk menggali lebih dalam mengenai persepsi pasien terhadap penyakit mereka dan bagaimana persepsi tersebut memengaruhi perilaku self-management mereka, termasuk faktor-faktor budaya dan sosial yang berperan. Ketiga, penelitian prospektif diperlukan untuk mengevaluasi dampak jangka panjang dari literasi kesehatan dan persepsi penyakit terhadap hasil klinis pasien hemodialisis, seperti tingkat kepatuhan terhadap diet, kontrol tekanan darah, dan kualitas hidup secara keseluruhan. Penelitian-penelitian ini diharapkan dapat memberikan bukti empiris yang kuat untuk pengembangan program edukasi dan dukungan yang lebih efektif bagi pasien hemodialisis, sehingga dapat meningkatkan kualitas hidup dan mengurangi risiko komplikasi yang terkait dengan penyakit ginjal kronis.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire: Psychology &... doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2015.1070851A systematic review and meta analysis of the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire Psychology doi 10 1080 08870446 2015 1070851
- The Relationship between Health Literacy, Illness Perception, and Self-Management Adherence among Hemodialysis... journalmpci.com/index.php/jhnr/article/view/401The Relationship between Health Literacy Illness Perception and Self Management Adherence among Hemodialysis journalmpci index php jhnr article view 401
- Advances in Nursing Science. advances nursing science doi.org/10.1097/ANS.0b013e318261b1baAdvances in Nursing Science advances nursing science doi 10 1097 ANS 0b013e318261b1ba
| File size | 418.19 KB |
| Pages | 10 |
| Short Link | https://juris.id/p-3dP |
| Lookup Links | Google ScholarGoogle Scholar, Semantic ScholarSemantic Scholar, CORE.ac.ukCORE.ac.uk, WorldcatWorldcat, ZenodoZenodo, Research GateResearch Gate, Academia.eduAcademia.edu, OpenAlexOpenAlex, Hollis HarvardHollis Harvard |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Dukungan keluarga secara signifikan meningkatkan perilaku perawatan diri pada pasien gagal jantung. Melibatkan anggota keluarga dalam program manajemenDukungan keluarga secara signifikan meningkatkan perilaku perawatan diri pada pasien gagal jantung. Melibatkan anggota keluarga dalam program manajemen
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI 8; 95% CI: 1. 9–4. 2), dan masalah hubungan sebaya (OR 1. 2–2. 9). Temuan ini memberikan dasar bukti untuk mengembangkan intervensi psikosocial komprehensif8; 95% CI: 1. 9–4. 2), dan masalah hubungan sebaya (OR 1. 2–2. 9). Temuan ini memberikan dasar bukti untuk mengembangkan intervensi psikosocial komprehensif
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Perlu dicatat, perawatan diri muncul sebagai prediktor yang lebih kuat. Temuan ini menyoroti peran penting baik spiritualitas maupun perawatan diri dalamPerlu dicatat, perawatan diri muncul sebagai prediktor yang lebih kuat. Temuan ini menyoroti peran penting baik spiritualitas maupun perawatan diri dalam
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Penelitian menggunakan desain survei cross‑sectional; populasi terdiri dari 369 wanita hamil, dengan teknik Simple Random Sampling menghasilkan 189 responden.Penelitian menggunakan desain survei cross‑sectional; populasi terdiri dari 369 wanita hamil, dengan teknik Simple Random Sampling menghasilkan 189 responden.
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI A sample of 100 pregnant women who experienced morning sickness in the first or second trimester, selected by purposive sampling at five Health CentersA sample of 100 pregnant women who experienced morning sickness in the first or second trimester, selected by purposive sampling at five Health Centers
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Kesimpulannya, penelitian ini memberikan kontribusi penting terhadap pengembangan pariwisata berbasis kesehatan di Bali, khususnya menekankan pentingnyaKesimpulannya, penelitian ini memberikan kontribusi penting terhadap pengembangan pariwisata berbasis kesehatan di Bali, khususnya menekankan pentingnya
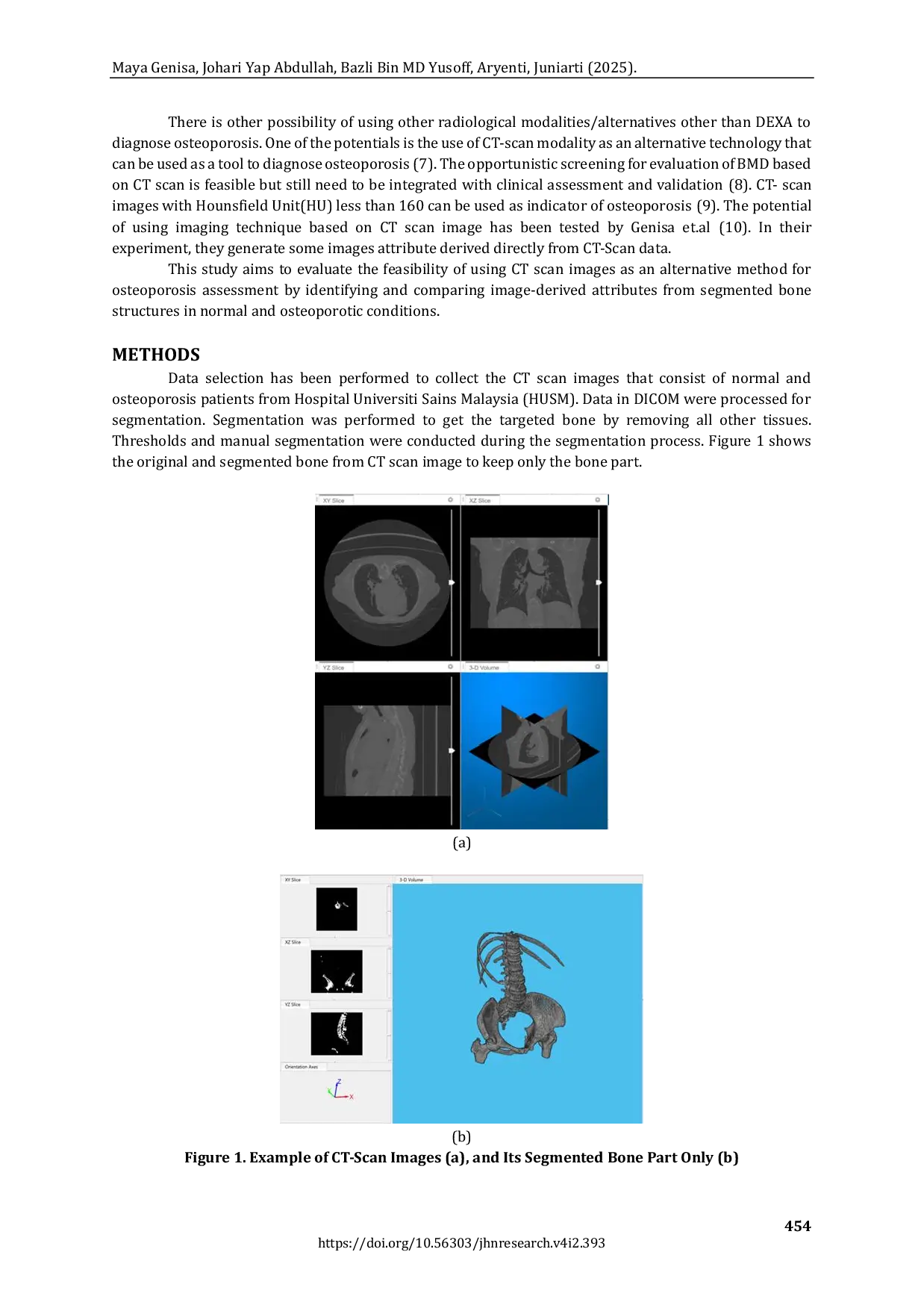
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Atribut Roughness dan Contrast cenderung menurun pada osteoporosis dibandingkan tulang normal, sedangkan atribut Phase dan Greyscale cenderung meningkatAtribut Roughness dan Contrast cenderung menurun pada osteoporosis dibandingkan tulang normal, sedangkan atribut Phase dan Greyscale cenderung meningkat
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Uji sensorik menunjukkan perlakuan J2 (50 g jamur) paling disukai panelis. Substitusi tinggi (75–100 g) mengurangi keterimaan sensorik karena aroma danUji sensorik menunjukkan perlakuan J2 (50 g jamur) paling disukai panelis. Substitusi tinggi (75–100 g) mengurangi keterimaan sensorik karena aroma dan
Useful /
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Coloring with Roselle and sappanwood can replace the use of watermelon flesh and can be further studied in relation to the functional characteristics thatColoring with Roselle and sappanwood can replace the use of watermelon flesh and can be further studied in relation to the functional characteristics that
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Tidak terdapat perbedaan signifikan pada kadar hemoglobin ibu hamil antara trimester pertama, namun terdapat perbedaan signifikan pada trimester ketigaTidak terdapat perbedaan signifikan pada kadar hemoglobin ibu hamil antara trimester pertama, namun terdapat perbedaan signifikan pada trimester ketiga
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI Pada tingkat keluarga, sanitasi yang tidak memadai (aOR 0,16; 95% CI: 0,03–0,84) dan kepemilikan aset yang lebih tinggi (aOR 0,13; 95% CI: 0,03–0,54).Pada tingkat keluarga, sanitasi yang tidak memadai (aOR 0,16; 95% CI: 0,03–0,84) dan kepemilikan aset yang lebih tinggi (aOR 0,13; 95% CI: 0,03–0,54).
JOURNALMPCIJOURNALMPCI 05 in the FPG examination and (p=0. 006) < 0. 05 in the 2-h PG examination. The oral antidiabetic drug groups metformin and glimepiride had differences05 in the FPG examination and (p=0. 006) < 0. 05 in the 2-h PG examination. The oral antidiabetic drug groups metformin and glimepiride had differences