LAPANLAPAN
Jurnal Teknologi DirgantaraJurnal Teknologi DirgantaraThe RX-450 rocket, developed by the Rocket Technology Center BRIN, serves various purposes, from sounding to military applications. This study focuses on estimating rocket velocity during the launch phase. Using MATLAB for image processing and OpenRocket for simulation, we explore the potential of image processing for velocity estimation, providing a cost-effective alternative. Results show velocity estimations trailing those of OpenRocket, attributed to friction force and setup differences. The study emphasizes the importance of camera positioning for accuracy. Despite differences, image processing shows promise, warranting further refinement.
This study demonstrated the potential of image processing methods for estimating rocket velocity during the launch phase, offering a cost-effective alternative.The results show a similar trend to simulations by OpenRocket, with differences attributed to setup variations and friction forces.The image processing approach has the potential to be further developed, but accuracy is influenced by factors such as camera orientation, calibration, and position.Future research should prioritize refining these aspects and developing improved filter methods to enhance the accuracy and reliability of velocity estimation through image processing.
Further research should investigate the use of stereo cameras to improve the accuracy of velocity estimation, addressing the limitations of single-camera setups. Additionally, exploring automated marker identification methods, such as utilizing the exhaust plume, could streamline the image processing workflow and reduce reliance on manual intervention. Finally, a comprehensive study on the impact of camera calibration and orientation on velocity estimation accuracy is needed, potentially incorporating machine learning techniques to optimize these parameters and develop a more robust and reliable system for rocket velocity measurement during launch, ultimately contributing to improved flight performance analysis and control.
| File size | 495.62 KB |
| Pages | 8 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
LAPANLAPAN Pengujian thermal dengan menggunakan thermal chamber VC3 4018 terhadap sensor analog selain berfungsi untuk mengukur temperatur dari APRS itu sendiri danPengujian thermal dengan menggunakan thermal chamber VC3 4018 terhadap sensor analog selain berfungsi untuk mengukur temperatur dari APRS itu sendiri dan
YASIN ALSYSYASIN ALSYS Penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa baik e-book maupun buku cetak secara positif berkontribusi terhadap kinerja akademik mahasiswa, dengan buku cetak memilikiPenelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa baik e-book maupun buku cetak secara positif berkontribusi terhadap kinerja akademik mahasiswa, dengan buku cetak memiliki
LAPANLAPAN Both equivalent models, Hoff and Reissner, significantly overestimate displacement, with Hoff underestimating stress and Reissner overestimating it. InBoth equivalent models, Hoff and Reissner, significantly overestimate displacement, with Hoff underestimating stress and Reissner overestimating it. In
IAIN KEDIRIIAIN KEDIRI Penelitian ini menunjukkan penggunaan pembelajaran bahasa berbasis web untuk mendorong mahasiswa berbicara Bahasa Inggris sebagai Bahasa Asing. MahasiswaPenelitian ini menunjukkan penggunaan pembelajaran bahasa berbasis web untuk mendorong mahasiswa berbicara Bahasa Inggris sebagai Bahasa Asing. Mahasiswa
UNIVMEDUNIVMED gonorrhoeae resistance to azithromycin reportedly occurs through two strategies, namely overexpression of the efflux pump (mutation of the mtrR codon region)gonorrhoeae resistance to azithromycin reportedly occurs through two strategies, namely overexpression of the efflux pump (mutation of the mtrR codon region)
NEWINERANEWINERA Users can be reached anytime, anywhere, and unused SMS credits are carried over. Messages are archived, and individuals can join groups by messaging theUsers can be reached anytime, anywhere, and unused SMS credits are carried over. Messages are archived, and individuals can join groups by messaging the
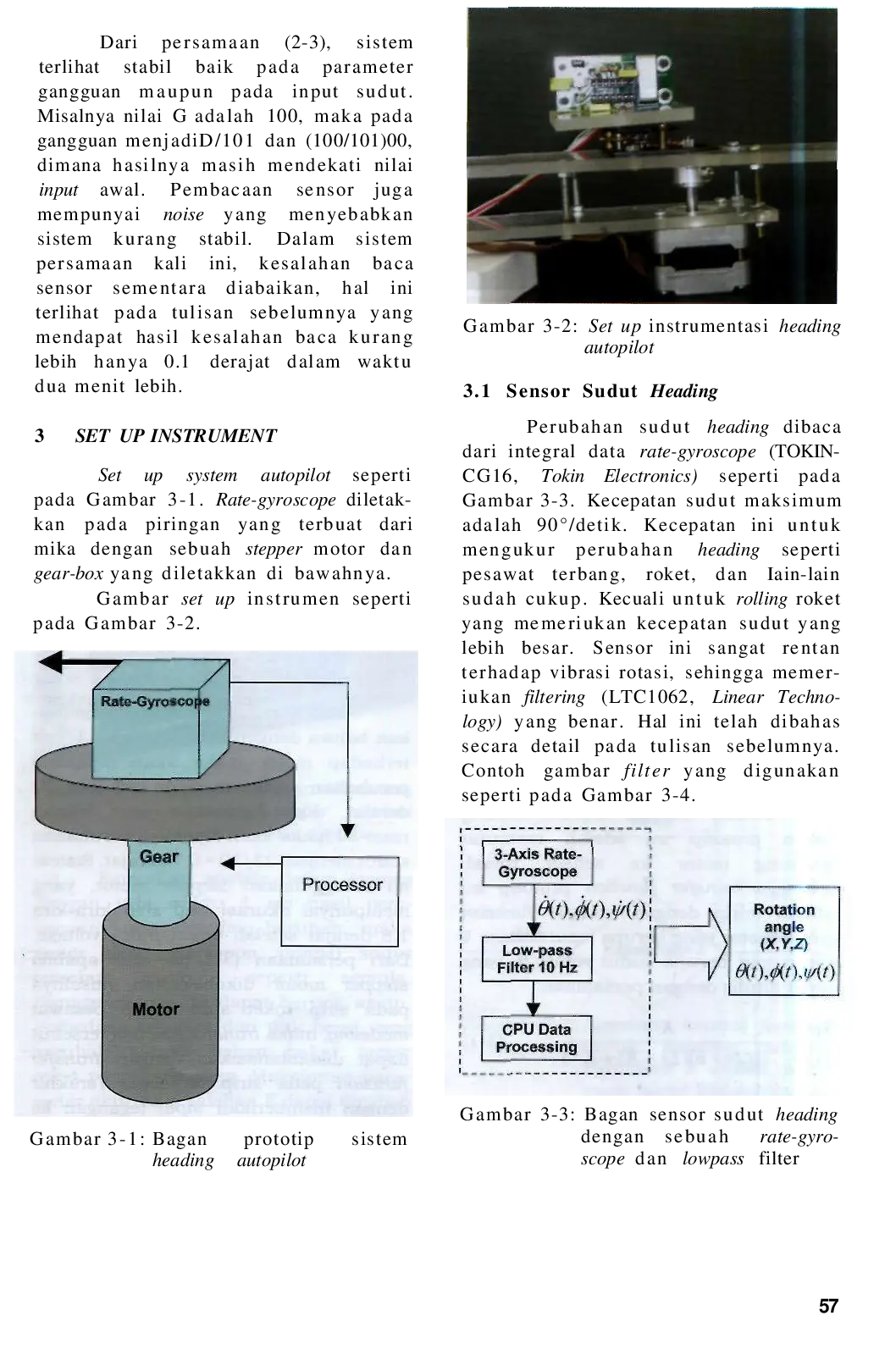
LAPANLAPAN Sistem ini telah berhasil direalisasikan dengan sudut kesalahan tidak lebih dari 0. 5° dari sudut heading, sehingga cukup akurat untuk wahana terbang.Sistem ini telah berhasil direalisasikan dengan sudut kesalahan tidak lebih dari 0. 5° dari sudut heading, sehingga cukup akurat untuk wahana terbang.
LAPANLAPAN Power meter radio mempunyai rentang pengukuran yang sempit, sehingga terjadi saturasi untuk pengukuran radio dengan power yang cukup besar. Tulisan iniPower meter radio mempunyai rentang pengukuran yang sempit, sehingga terjadi saturasi untuk pengukuran radio dengan power yang cukup besar. Tulisan ini
Useful /
PAEDIATRICAINDONESIANAPAEDIATRICAINDONESIANA Aktivitas Brain Gym® telah terbukti meningkatkan koordinasi motorik, rentang perhatian, dan keterampilan motorik halus pada anak-anak prasekolah dan sekolahAktivitas Brain Gym® telah terbukti meningkatkan koordinasi motorik, rentang perhatian, dan keterampilan motorik halus pada anak-anak prasekolah dan sekolah
PAEDIATRICAINDONESIANAPAEDIATRICAINDONESIANA Faktor-faktor yang berkontribusi terhadap keterlambatan pemberian EN meliputi operasi abdomen, penggunaan ventilator, penggunaan inotropik, gejala gastrointestinal,Faktor-faktor yang berkontribusi terhadap keterlambatan pemberian EN meliputi operasi abdomen, penggunaan ventilator, penggunaan inotropik, gejala gastrointestinal,
STIE AASSTIE AAS Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan analisis data kuantitatif dengan uji menggunakan Model Regresi Linear Berganda. Populasi dalam penelitian ini meliputiPenelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan analisis data kuantitatif dengan uji menggunakan Model Regresi Linear Berganda. Populasi dalam penelitian ini meliputi
LAPANLAPAN Zona 1, daerah yang paling berbahaya berjarak 0 - 3 m, dan zona 2, 3 - 40 m, adalah daerah yang masih dipengaruhi oleh gas-gas berbahaya. Pengamatan langsungZona 1, daerah yang paling berbahaya berjarak 0 - 3 m, dan zona 2, 3 - 40 m, adalah daerah yang masih dipengaruhi oleh gas-gas berbahaya. Pengamatan langsung