PHBPHB
Jurnal Ners dan Kebidanan (Journal of Ners and Midwifery)Jurnal Ners dan Kebidanan (Journal of Ners and Midwifery)Optimal breastfeeding practices play a crucial role in enhancing the health of infants and children. However, increased anxiety among postpartum mothers can lead to higher cortisol levels. Moxibustion is a traditional therapy that has been shown to improve blood circulation, reduce discomfort, and influence the central nervous system by stimulating specific meridian points. This study aimed to examine the effect of moxibustion on cortisol levels in breastfeeding mothers. A quasi-experimental design with pretest and posttest was used. Participants were divided into two groups: an intervention group that received moxibustion and a control group that received acupuncture. A total of 32 breastfeeding mothers from Ngaliyan Public Health Center in Semarang participated in the study, with 16 individuals in each group. Moxibustion was applied to specific meridian points (CV17, LI4, SP6, ST16, ST18, ST36, BL17, and BL18). Cortisol levels were measured using the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method, and data were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test. The results showed no significant difference in cortisol levels between the two groups (p = 0.864). The average cortisol change was -0.063 in the intervention group and -0.113 in the control group. It was concluded that moxibustion had no significant effect on cortisol levels. Further studies are recommended to explore other factors that may influence cortisol levels in postpartum mothers.
The study found no significant difference in cortisol levels between the moxibustion and acupressure groups, indicating that neither treatment effectively reduced cortisol levels in breastfeeding mothers.The occupation of the mothers was found to influence cortisol levels, suggesting that work-related stress may play a role.Therefore, further research is needed to investigate other factors that may affect cortisol levels in postpartum mothers.
Penelitian lebih lanjut perlu dilakukan untuk mengidentifikasi faktor-faktor lain yang dapat memengaruhi kadar kortisol pada ibu menyusui, seperti dukungan sosial, kualitas tidur, dan pola makan. Studi di masa depan dapat mengeksplorasi kombinasi terapi moksibusi dengan intervensi lain, seperti konseling psikologis atau teknik relaksasi, untuk melihat apakah pendekatan multimodal dapat memberikan hasil yang lebih baik dalam mengurangi stres dan kecemasan pada ibu postpartum. Selain itu, penelitian dengan desain studi yang lebih kuat, seperti uji klinis acak terkontrol dengan ukuran sampel yang lebih besar, diperlukan untuk mengkonfirmasi temuan ini dan memberikan bukti yang lebih meyakinkan tentang efektivitas moksibusi dalam memodulasi kadar kortisol pada ibu menyusui. Penelitian ini diharapkan dapat memberikan wawasan yang lebih mendalam tentang bagaimana meningkatkan kesejahteraan mental dan fisik ibu menyusui, yang pada akhirnya akan berdampak positif pada kesehatan bayi mereka.
- The Effect Of Lactation Massage On Breast Milk Production In Breastfeeding Mothers | Jurnal Midpro. effect... doi.org/10.30736/md.v15i2.692The Effect Of Lactation Massage On Breast Milk Production In Breastfeeding Mothers Jurnal Midpro effect doi 10 30736 md v15i2 692
- Respons molekuler beta endorphin terhadap variasi intensitas latihan pada atlet sprint | Jurnal Keolahragaan.... journal.uny.ac.id/index.php/jolahraga/article/view/33833Respons molekuler beta endorphin terhadap variasi intensitas latihan pada atlet sprint Jurnal Keolahragaan journal uny ac index php jolahraga article view 33833
- Effect of Acupressure, Acupuncture and Moxibustion in Women With Pregnancy-Related Anxiety and Previous... doi.org/10.14740/jocmr3009wEffect of Acupressure Acupuncture and Moxibustion in Women With Pregnancy Related Anxiety and Previous doi 10 14740 jocmr3009w
- Hubungan Status Pekerjaan Ibu dengan Pemberian ASI Eksklusif di Wilayah Kerja UPT Puskesmas Menteng Tahun... doi.org/10.33084/jsm.v9i1.5160Hubungan Status Pekerjaan Ibu dengan Pemberian ASI Eksklusif di Wilayah Kerja UPT Puskesmas Menteng Tahun doi 10 33084 jsm v9i1 5160
| File size | 424.72 KB |
| Pages | 9 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
PSPPJOURNALSPSPPJOURNALS Penelitian ini tidak hanya memberikan dukungan empiris mengenai keberhasilan instrumen strategis terintegrasi dalam lingkungan layanan publik, tetapi jugaPenelitian ini tidak hanya memberikan dukungan empiris mengenai keberhasilan instrumen strategis terintegrasi dalam lingkungan layanan publik, tetapi juga
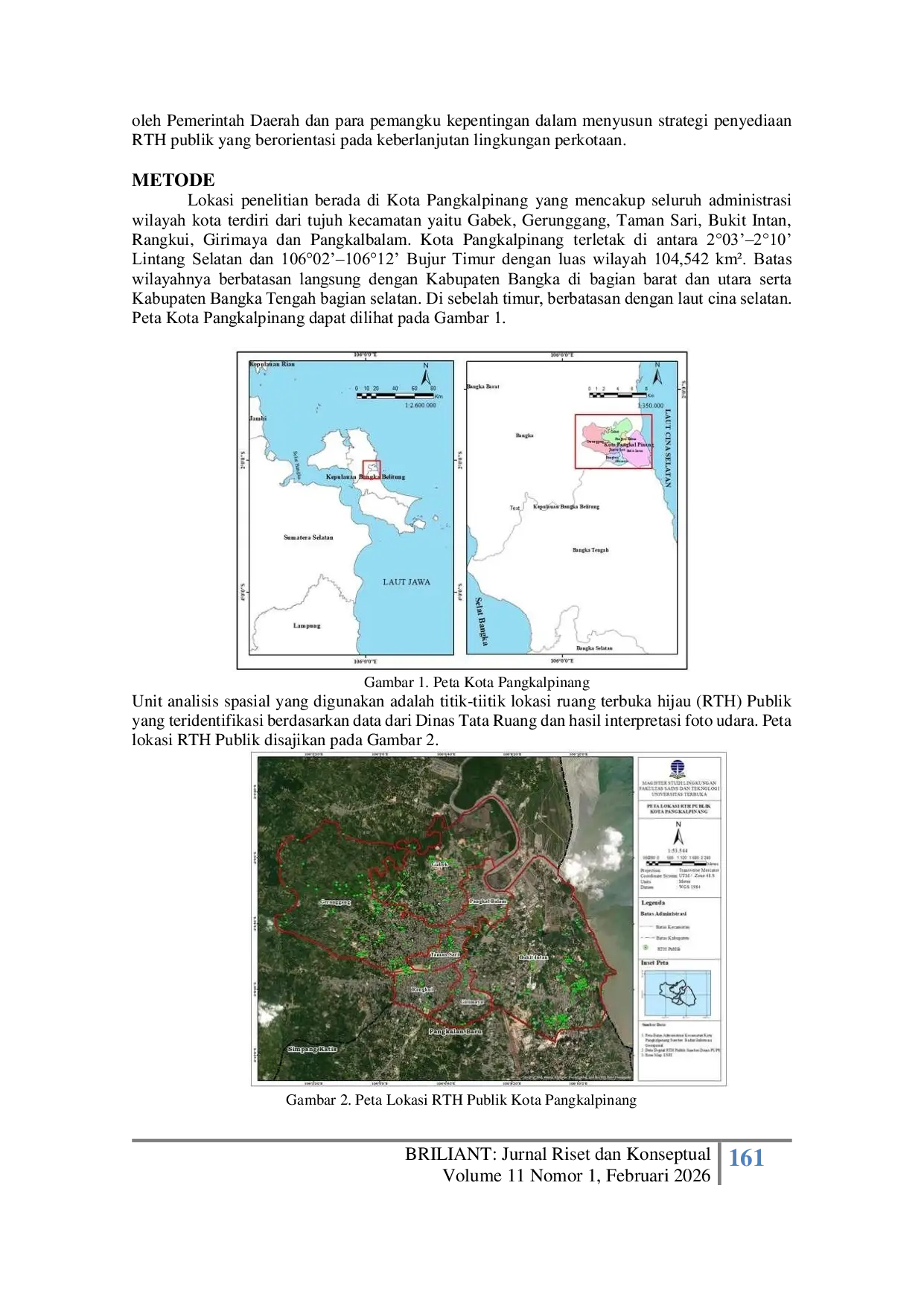
UNUBLITARUNUBLITAR Di kota Pangkalpinang pertumbuhan kawasan terbangun yang pesat menimbulkan tantangan terhadap proporsional dan distribusi RTH yang ideal. Penelitian iniDi kota Pangkalpinang pertumbuhan kawasan terbangun yang pesat menimbulkan tantangan terhadap proporsional dan distribusi RTH yang ideal. Penelitian ini
AZZUKHRUFCENDIKIAAZZUKHRUFCENDIKIA Penelitian ini dilakukan dengan menyebarkan kuesioner kepada admin proyek, staf, dan PIC proyek di PT. Deksha Orla Tranggana, yaitu 39 kuesioner yang disebarkanPenelitian ini dilakukan dengan menyebarkan kuesioner kepada admin proyek, staf, dan PIC proyek di PT. Deksha Orla Tranggana, yaitu 39 kuesioner yang disebarkan
IAIQHIAIQH Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kuantitatif dengan metode quasi eksperimen jenis non-equivalent control group design. Hasil penelitian menunjukkanPenelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kuantitatif dengan metode quasi eksperimen jenis non-equivalent control group design. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan
UMLAUMLA Hypertension in the elderly is a growing global health problem, influenced by factors like low vegetable consumption. This study aims to determine theHypertension in the elderly is a growing global health problem, influenced by factors like low vegetable consumption. This study aims to determine the
UHBUHB Namun, masih ada celah hukum, terutama dalam regulasi terkait praktik mandiri dan Puskesmas yang tidak secara eksplisit mengatur kewajiban layanan darurat.Namun, masih ada celah hukum, terutama dalam regulasi terkait praktik mandiri dan Puskesmas yang tidak secara eksplisit mengatur kewajiban layanan darurat.
UDSUDS Penelitian menunjukkan bahwa pengetahuan orang tua setelah diberikan edukasi lebih tinggi dibandingkan sebelum diberikan edukasi. Rata-rata pengetahuanPenelitian menunjukkan bahwa pengetahuan orang tua setelah diberikan edukasi lebih tinggi dibandingkan sebelum diberikan edukasi. Rata-rata pengetahuan
BELITUNG RAYABELITUNG RAYA Conclusion: There was a significant effect of green bean (Phaseolus Radiatus) juice in increasing the levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythrocytes.Conclusion: There was a significant effect of green bean (Phaseolus Radiatus) juice in increasing the levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythrocytes.
Useful /
PHBPHB Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengkaji korelasi antara pengetahuan kesehatan reproduksi dengan sikap remaja terhadap persepsi pernikahan dini. MetodePenelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengkaji korelasi antara pengetahuan kesehatan reproduksi dengan sikap remaja terhadap persepsi pernikahan dini. Metode
IAIQHIAIQH Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui profil kemampuan liteasi sains dari siswa. Sampel dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas V di Madrasah IbtidaiyahPenelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui profil kemampuan liteasi sains dari siswa. Sampel dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas V di Madrasah Ibtidaiyah
UIN MATARAMUIN MATARAM Dengan kepercayaan tersebut, lahir berbagai acara tradisional yang erat kaitannya dengan pelestarian hutan dan lingkungan tempat mereka tinggal. KetigaDengan kepercayaan tersebut, lahir berbagai acara tradisional yang erat kaitannya dengan pelestarian hutan dan lingkungan tempat mereka tinggal. Ketiga
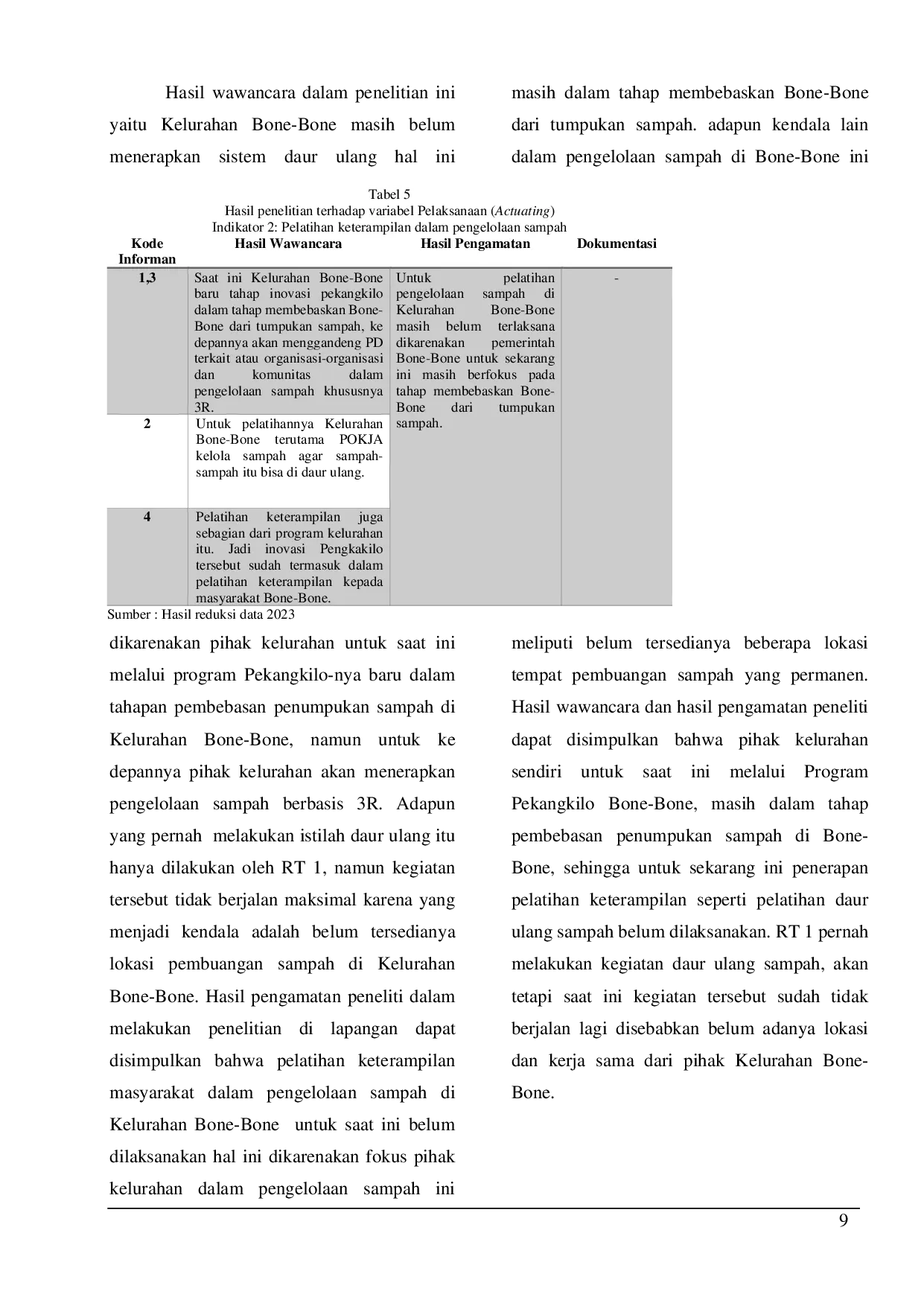
LPPMUNIDAYANLPPMUNIDAYAN Berdasarkan hasil penelitian dan pembahasan yang telah dilakukan, peneliti menarik kesimpulan bahwa pengelolaan sampah di Kelurahan Bone-Bone telah mengalamiBerdasarkan hasil penelitian dan pembahasan yang telah dilakukan, peneliti menarik kesimpulan bahwa pengelolaan sampah di Kelurahan Bone-Bone telah mengalami