STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI
JKBLJKBLWhite blood cell (WBC) classification plays a crucial role in hematological diagnosis and is typically performed manually using microscopic images. However, manual analysis is limited by subjectivity and time inefficiency. With recent technological advances, artificial intelligence (AI) offers promising solutions for automated WBC classification that enhance accuracy and efficiency. This study presents a scoping review of 20 scientific publications discussing AI applications in microscopic image-based WBC classification. Literature searches were conducted in PubMed, ScienceDirect, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Xplore, and Google Scholar using relevant keywords such as “AI, “white blood cell, and “microscopic image. Findings indicate that the most commonly used method is Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), either standalone or hybrid (e.g., YOLOv5, ResNet, Vision Transformer), achieving accuracies up to 99.7%. The datasets were mostly public Blood Cell Count and Detection (BCCD), Leucocyte Images for Segmentation and Classification (LISC), Raabin-WBC or local laboratory sources. The reviewed studies aimed at automatic WBC detection, classification, and morphological identification. Despite encouraging outcomes, challenges such as external validation and limited access to real clinical data remain. Overall, AI has proven effective in enhancing speed, accuracy, and objectivity in WBC classification. Further research is needed to support AI integration into real-world clinical laboratory practice.
This scoping review demonstrates the effectiveness of deep learning models, particularly CNNs, in enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of white blood cell classification using microscopic images.While AI shows promise in improving objectivity and reproducibility in hematological diagnostics, challenges related to external validation and the limited availability of diverse clinical data remain.Ultimately, the successful integration of AI into clinical practice requires strategic efforts focused on generalizability, interpretability, and adherence to regulatory standards.
Future research should prioritize the creation and standardization of larger, more diverse datasets of microscopic blood cell images, encompassing various populations to improve the generalizability of AI models. Furthermore, rigorous external validation studies are crucial to assess the performance of these models across different laboratory settings and patient demographics, ensuring their reliability in real-world clinical applications. Finally, developing user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training programs for healthcare professionals will be essential to facilitate the seamless integration of AI-powered tools into routine hematological workflows, ultimately enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency while minimizing the potential for misinterpretation and maximizing clinical impact. These advancements will pave the way for more objective, efficient, and accessible hematological diagnostics, benefiting both clinicians and patients.
| File size | 196.88 KB |
| Pages | 8 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
IAIN KEDIRIIAIN KEDIRI Penelitian ini mengeksplorasi perspektif guru EFL tingkat universitas di Kurdistan tentang faktor yang memengaruhi pilihan metode penilaian, tantanganPenelitian ini mengeksplorasi perspektif guru EFL tingkat universitas di Kurdistan tentang faktor yang memengaruhi pilihan metode penilaian, tantangan
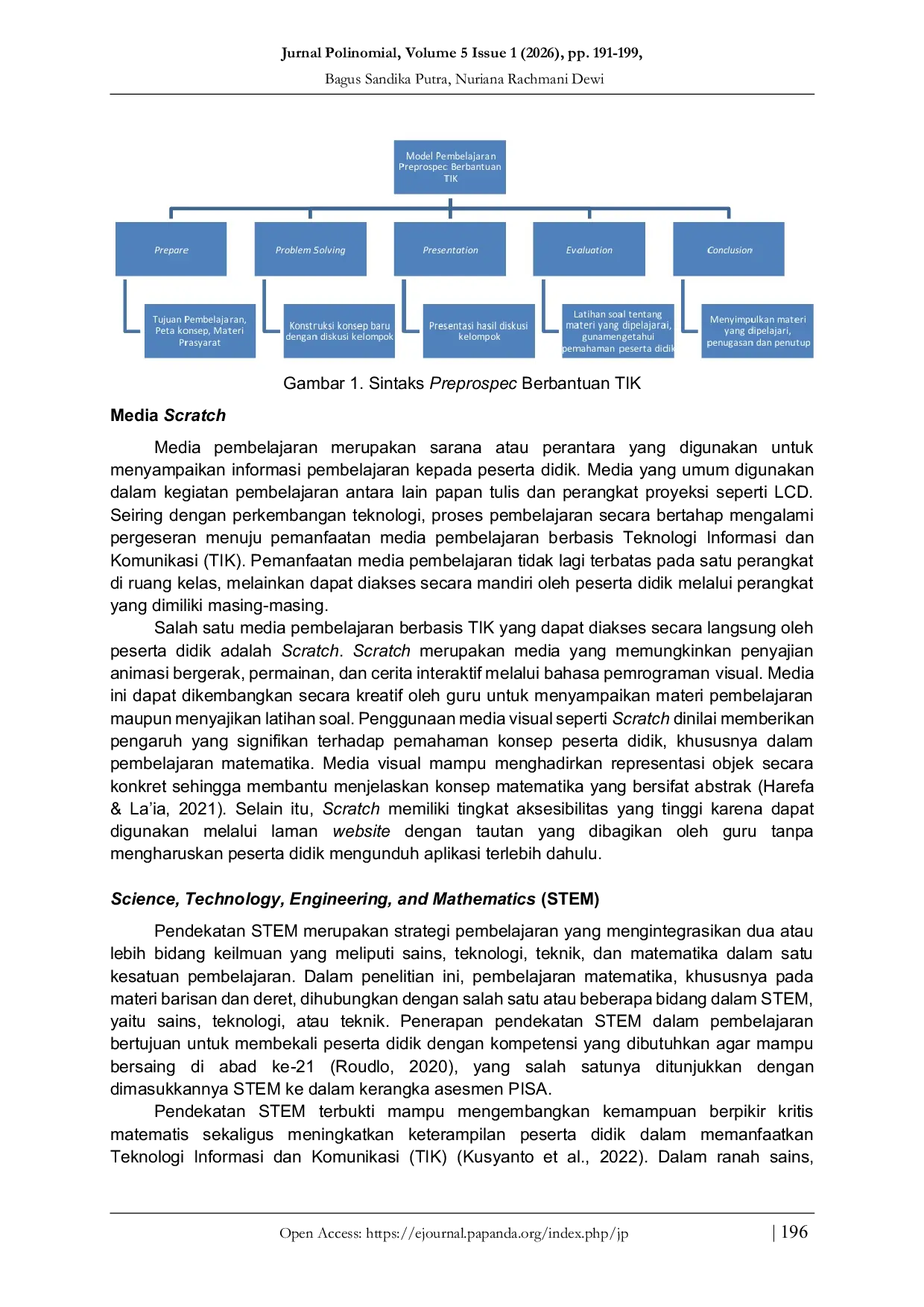
PAPANDAPAPANDA Model pembelajaran Preprospec berbantuan TIK terbukti relevan dalam meningkatkan kemampuan tersebut karena sintaks pembelajarannya mendorong peserta didikModel pembelajaran Preprospec berbantuan TIK terbukti relevan dalam meningkatkan kemampuan tersebut karena sintaks pembelajarannya mendorong peserta didik
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Namun, hal ini tidak berarti konsumsi makanan cepat saji tidak relevan dengan kesehatan, tetapi menunjukkan bahwa faktor lain seperti aktivitas fisik,Namun, hal ini tidak berarti konsumsi makanan cepat saji tidak relevan dengan kesehatan, tetapi menunjukkan bahwa faktor lain seperti aktivitas fisik,
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Data dianalisis dengan uji T berpasangan. Hasil menunjukkan bahwa kualitas tidur rata-rata sebelum intervensi adalah 5,6 dengan kualitas tidur buruk, danData dianalisis dengan uji T berpasangan. Hasil menunjukkan bahwa kualitas tidur rata-rata sebelum intervensi adalah 5,6 dengan kualitas tidur buruk, dan
IAIDAIAIDA Studi ini berfokus pada konsep Total Quality Management (TQM) yang menekankan perbaikan berkelanjutan, keterlibatan semua pihak, dan evaluasi konsisten.Studi ini berfokus pada konsep Total Quality Management (TQM) yang menekankan perbaikan berkelanjutan, keterlibatan semua pihak, dan evaluasi konsisten.
POLTEKKESKUPANGPOLTEKKESKUPANG The sample was the elderly who live in nursing homes. This study employed simple random sampling with a total sample of 116 people in 2 provinces: DKIThe sample was the elderly who live in nursing homes. This study employed simple random sampling with a total sample of 116 people in 2 provinces: DKI
POLTEKKESKUPANGPOLTEKKESKUPANG The results of this study revealed the projection of Acid Resistant Bacteria Positive Pulmonary TB cases based on gender, health centers, hospitals, andThe results of this study revealed the projection of Acid Resistant Bacteria Positive Pulmonary TB cases based on gender, health centers, hospitals, and
POLTEKKESKUPANGPOLTEKKESKUPANG Penelitian ini bertujuan mengukur efek antioksidan ekstrak etanol daun velvet kuning (Limnocharis Flava) pada aktivitas Malondialdehyde (MDA) di jaringanPenelitian ini bertujuan mengukur efek antioksidan ekstrak etanol daun velvet kuning (Limnocharis Flava) pada aktivitas Malondialdehyde (MDA) di jaringan
Useful /
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Statistical data from the BKKBN shows that the achievement of new KB participants has decreased significantly. The purpose of the study was to determineStatistical data from the BKKBN shows that the achievement of new KB participants has decreased significantly. The purpose of the study was to determine
IAI TABAHIAI TABAH Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 19 warga telah berpartisipasi dalam donor ASI. Dari jumlah tersebut, 10 individu termasuk dalam kategori mahram menurutHasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 19 warga telah berpartisipasi dalam donor ASI. Dari jumlah tersebut, 10 individu termasuk dalam kategori mahram menurut
IAI TABAHIAI TABAH Dzikir tidak hanya membantu individu mencapai ketenangan jiwa melalui ingatan akan Allah, tetapi juga memiliki implikasi spiritual yang mendalam denganDzikir tidak hanya membantu individu mencapai ketenangan jiwa melalui ingatan akan Allah, tetapi juga memiliki implikasi spiritual yang mendalam dengan
IAI TABAHIAI TABAH Kajian ini menyumbang dalam mengetengahkan idea yang dikembangkannya dalam tradisi pemikiran Islam moden dari segi perancangan dan pengaplikasian dasar-dasarKajian ini menyumbang dalam mengetengahkan idea yang dikembangkannya dalam tradisi pemikiran Islam moden dari segi perancangan dan pengaplikasian dasar-dasar