ESDMESDM
Indonesian Journal on GeoscienceIndonesian Journal on GeoscienceNorthern Thailand is an active tectonic region with a history of low to medium magnitude earthquakes, including the Mw 6.1 Mae Lao Earthquake in 2014 which resulted in liquefaction. This research investigates liquefaction potential using seismic ground response analysis, incorporating standard penetration tests and seismic down-hole tests in Chiang Rai Province. A next-generation attenuation model was used to generate ground motion for nonlinear seismic response analysis. The peak ground acceleration at the ground surface, derived from the analysis, was used to assess liquefaction potential empirically. The results indicate that liquefaction could occur at the investigated locations during the earthquake, confirming observations from the Mae Lao Earthquake. This research aims to inform considerations of earthquake impacts in Northern Thailand.
The study reveals that northern Thailand, particularly Chiang Rai Province with its sandy soil profile, is susceptible to liquefaction during earthquakes.The analysis, based on seismic ground response and empirical methods, indicates liquefaction potential at several investigated sites, particularly those close to the earthquake epicenter.These findings underscore the importance of considering liquefaction hazards in seismic design and mitigation strategies for the region.
Berdasarkan penelitian ini, beberapa saran penelitian lanjutan dapat diajukan untuk memperdalam pemahaman dan meningkatkan ketahanan wilayah utara Thailand terhadap gempa bumi. Pertama, perlu dilakukan studi lebih lanjut mengenai pengaruh variasi lapisan tanah yang kompleks terhadap amplifikasi gempa dan potensi likuifaksi. Hal ini dapat dilakukan dengan menggunakan metode pemodelan yang lebih canggih, seperti analisis elemen hingga (finite element analysis), untuk mensimulasikan interaksi antara berbagai lapisan tanah dan meramalkan respons dinamisnya secara lebih akurat. Kedua, penelitian tentang pengaruh kondisi air tanah terhadap likuifaksi perlu diperluas dengan mempertimbangkan variasi muka air tanah musiman dan dampaknya terhadap tekanan air pori. Pengukuran dan pemantauan muka air tanah secara berkala dapat memberikan data yang lebih komprehensif untuk memvalidasi model-model likuifaksi. Ketiga, penting untuk mengembangkan sistem peringatan dini likuifaksi yang terintegrasi dengan sistem peringatan dini gempa bumi. Sistem ini dapat memanfaatkan data dari sensor-sensor gempa bumi dan sensor-sensor tanah untuk mendeteksi potensi likuifaksi secara real-time dan memberikan peringatan kepada masyarakat sebelum terjadinya gempa bumi.
| File size | 4.64 MB |
| Pages | 13 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
POLMAN BABELPOLMAN BABEL Berdasarkan data ini, ITRS menyesuaikan suhu dan aliran udara untuk menjaga kenyamanan optimal sekaligus meminimalkan penggunaan energi. Hasil percobaanBerdasarkan data ini, ITRS menyesuaikan suhu dan aliran udara untuk menjaga kenyamanan optimal sekaligus meminimalkan penggunaan energi. Hasil percobaan
IAIIIAII Informasi yang terhimpun dijadikan sebagai dasar dalam pengambilan keputusan. Namun tidak semua informasi dapat langsung digunakan untuk proses pengambilanInformasi yang terhimpun dijadikan sebagai dasar dalam pengambilan keputusan. Namun tidak semua informasi dapat langsung digunakan untuk proses pengambilan
POLTEKKES JAKARTA 3POLTEKKES JAKARTA 3 Teknik pengumpulan data menggunakan kuesioner. Intervensi edukasi simulasi bencana gempa bumi dilakukan dua kali pada satu kali pertemuan selama 2x120Teknik pengumpulan data menggunakan kuesioner. Intervensi edukasi simulasi bencana gempa bumi dilakukan dua kali pada satu kali pertemuan selama 2x120
LAPANLAPAN Untuk ketahanan modul APRSnya sendiri, pada temperatur dari -20°C sampai 60°C masih berjalan dengan baik, sehingga modul APRS masih dianggap tahan padaUntuk ketahanan modul APRSnya sendiri, pada temperatur dari -20°C sampai 60°C masih berjalan dengan baik, sehingga modul APRS masih dianggap tahan pada
UIGMUIGM Peserta juga berhasil mengidentifikasi pola risiko kehamilan dan mengelompokkan data pasien berdasarkan karakteristik klinis, yang dapat mendukung pengambilanPeserta juga berhasil mengidentifikasi pola risiko kehamilan dan mengelompokkan data pasien berdasarkan karakteristik klinis, yang dapat mendukung pengambilan
YBLIYBLI Sebelum kegiatan peserta dilakukan pretest untuk mengetahui tingkat pengetahuan peserta tentang tanggap darurat bencana: Transportasi dan Evakuasi. PesertaSebelum kegiatan peserta dilakukan pretest untuk mengetahui tingkat pengetahuan peserta tentang tanggap darurat bencana: Transportasi dan Evakuasi. Peserta
ITBITB Hasil menunjukkan bahwa kertas dengan komposisi 70% serat kulit pisang dan 30% serat kayu menghasilkan kekuatan tarik dan daya serap air yang memenuhiHasil menunjukkan bahwa kertas dengan komposisi 70% serat kulit pisang dan 30% serat kayu menghasilkan kekuatan tarik dan daya serap air yang memenuhi
ITBITB Kertas ini juga menunjukkan ketahanan air yang lebih baik dibanding kertas daur ulang. Penelitian ini memberi bukti bahwa kulit pisang dapat dimanfaatkanKertas ini juga menunjukkan ketahanan air yang lebih baik dibanding kertas daur ulang. Penelitian ini memberi bukti bahwa kulit pisang dapat dimanfaatkan
Useful /
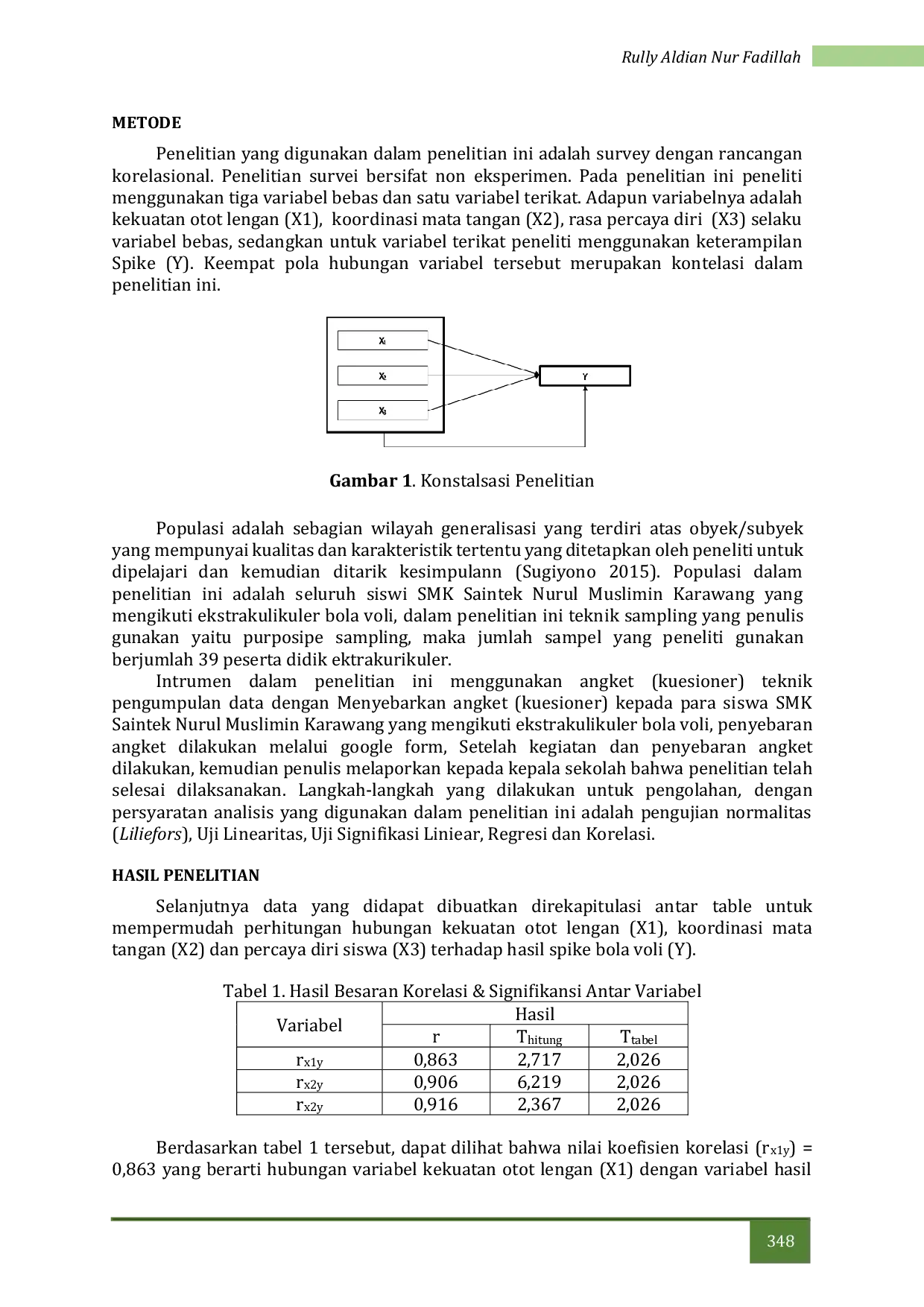
STKIP PASUNDANSTKIP PASUNDAN Variabel koordinasi diukur dengan instrument wall past test, sementara keterampilan bola voli di ukur dengan spike, angket digunakan untuk penilaian kepercayaanVariabel koordinasi diukur dengan instrument wall past test, sementara keterampilan bola voli di ukur dengan spike, angket digunakan untuk penilaian kepercayaan
STKIP PASUNDANSTKIP PASUNDAN Berdasarkan analisis data dan pembahasannya, maka dari hasil penelitian ini penulis dapat menyimpulkan bahwa terdapat hubungan yang signifikan antara mediaBerdasarkan analisis data dan pembahasannya, maka dari hasil penelitian ini penulis dapat menyimpulkan bahwa terdapat hubungan yang signifikan antara media
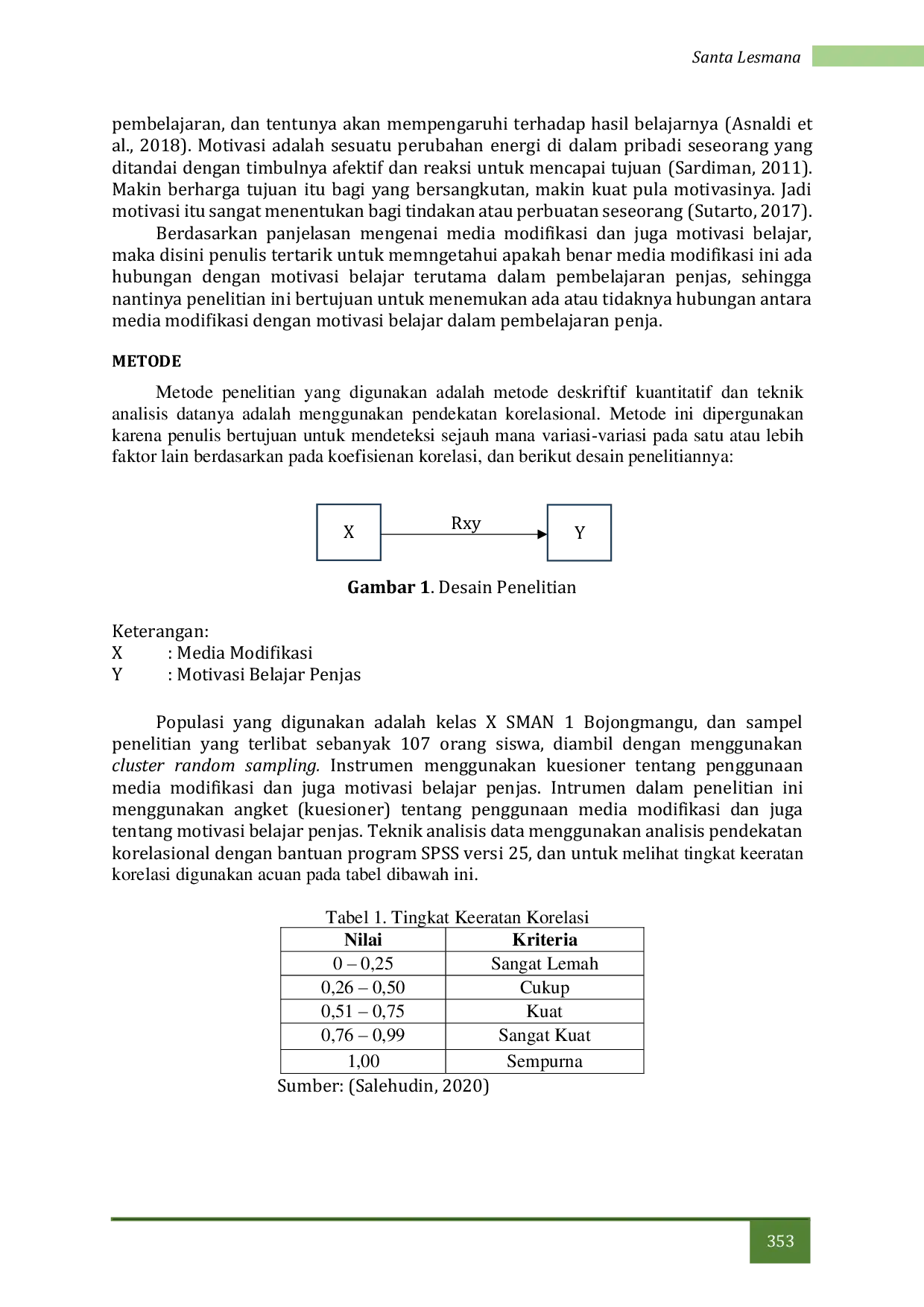
ITBITB Menggunakan metode kuasi eksperimen dengan desain pretest-posttest control group, sampel terdiri dari 60 siswa kelas XI di salah satu SMA Negeri di KotaMenggunakan metode kuasi eksperimen dengan desain pretest-posttest control group, sampel terdiri dari 60 siswa kelas XI di salah satu SMA Negeri di Kota
ITBITB Metode penelitian yang digunakan adalah kuasi eksperimen dengan desain pretest-posttest control group design. Populasi penelitian adalah seluruh siswaMetode penelitian yang digunakan adalah kuasi eksperimen dengan desain pretest-posttest control group design. Populasi penelitian adalah seluruh siswa