UBUB
Heart Science JournalHeart Science JournalCOVID-19 has become a major public health problem, with new cases and deaths growing around the world. COVID-19 has been reported to associate with a hypercoagulable state, which may lead to venous thromboembolism (VTE) formation. This condition is also associated with worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients. It is, therefore, critical for clinicians to identify this condition and manage accordingly. VTE formation in COVID-19 occurs through several mechanisms, such as inflammatory reaction leading to a hypercoagulable state and vascular dysfunction and direct vascular injury by the virus. The rate of VTE formation was as high as 31% in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients and 9.2% in general wards patients. It was also associated with poor prognosis. Thromboprophylaxis with heparin, particularly low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), has been shown to improve these patients prognosis. A careful individual assessment is required to determine which patients will benefit from this therapy. There are still no sufficient prospective trials to establish guidelines for VTE thrombo-prophylaxis in COVID-19. The assessment includes laboratory parameters such as PT, platelet count, D-dimer, fibrinogen, and other risk factors incorporated in the PADUA risk assessment model (RAM), versus the risk of bleeding incorporated in IMPROVE bleeding RAM.
Patients with COVID-19 are at increased risk of VTE due to inflammatory reactions, vascular dysfunction, and direct viral injury.Thromboprophylaxis with heparin, especially LMWH, can improve patient outcomes.A thorough individual assessment, considering both VTE risk factors and bleeding risks, is crucial for determining appropriate therapy.
Penelitian lebih lanjut perlu dilakukan untuk mengidentifikasi biomarker yang lebih akurat untuk memprediksi risiko VTE pada pasien COVID-19, sehingga memungkinkan stratifikasi risiko yang lebih tepat dan personalisasi terapi antikoagulan. Studi prospektif yang terkontrol dengan baik sangat dibutuhkan untuk mengevaluasi efektivitas dan keamanan berbagai strategi tromboprofilaksis, termasuk dosis LMWH yang optimal, pada populasi pasien COVID-19 yang beragam, dengan mempertimbangkan faktor-faktor seperti tingkat keparahan penyakit, komorbiditas, dan risiko perdarahan. Selain itu, penelitian juga perlu menyelidiki peran potensial terapi anti-inflamasi sebagai pendekatan tambahan untuk mencegah VTE pada pasien COVID-19, karena peradangan yang berlebihan merupakan pendorong utama hiperkoagulasi dalam konteks ini. Studi-studi ini dapat membantu menyempurnakan pedoman klinis dan meningkatkan hasil bagi pasien yang terinfeksi COVID-19.
| File size | 1.35 MB |
| Pages | 5 |
| DMCA | ReportReport |
Related /
UBUB Peran CCTA telah berkembang dari alat diagnostik anatomi menjadi pilar sentral dalam pencegahan kardiovaskular yang dipersonalisasi. Kemampuannya untukPeran CCTA telah berkembang dari alat diagnostik anatomi menjadi pilar sentral dalam pencegahan kardiovaskular yang dipersonalisasi. Kemampuannya untuk
UBUB Pada tindak lanjut 12 bulan, tingkat mortalitas (4,6% vs. 13,8% vs. 21,7%; p = 0,015) dan rawat inap (15,4% vs. 20,7% vs. 42%; p = 0,001) lebih tinggiPada tindak lanjut 12 bulan, tingkat mortalitas (4,6% vs. 13,8% vs. 21,7%; p = 0,015) dan rawat inap (15,4% vs. 20,7% vs. 42%; p = 0,001) lebih tinggi
UBUB Kami memutuskan untuk menggunakan arteri femoralis kanan sebagai akses. Kami melanjutkan prosedur dua hari kemudian, di bawah anestesi umum, angiografiKami memutuskan untuk menggunakan arteri femoralis kanan sebagai akses. Kami melanjutkan prosedur dua hari kemudian, di bawah anestesi umum, angiografi
UBUB Pasien didiagnosis AIHA dengan hasil tes Coombs langsung positif. Group 5 hipertensi paru terbentuk berdasarkan hasil pemeriksaan fisik, radiologi dada,Pasien didiagnosis AIHA dengan hasil tes Coombs langsung positif. Group 5 hipertensi paru terbentuk berdasarkan hasil pemeriksaan fisik, radiologi dada,
Useful /
UNISLAUNISLA Penelitian ini menggarisbawahi dampak positif kuis daring terhadap peningkatan keterlibatan, motivasi, dan efektivitas belajar siswa dalam mata kuliahPenelitian ini menggarisbawahi dampak positif kuis daring terhadap peningkatan keterlibatan, motivasi, dan efektivitas belajar siswa dalam mata kuliah
UBUB Hiperglikemia dan diabetes melitus banyak dijumpai pada pasien STEMI yang dirawat di rumah sakit. Hemoglobin terglikasi (HbA1c) adalah penanda kontrolHiperglikemia dan diabetes melitus banyak dijumpai pada pasien STEMI yang dirawat di rumah sakit. Hemoglobin terglikasi (HbA1c) adalah penanda kontrol
LAPANLAPAN Generator turbin angin merupakan salah satu bagian/komponen dari turbin angin yang berfungsi mengkonversi energi mekanik menjadi energi listrik dan memilikiGenerator turbin angin merupakan salah satu bagian/komponen dari turbin angin yang berfungsi mengkonversi energi mekanik menjadi energi listrik dan memiliki
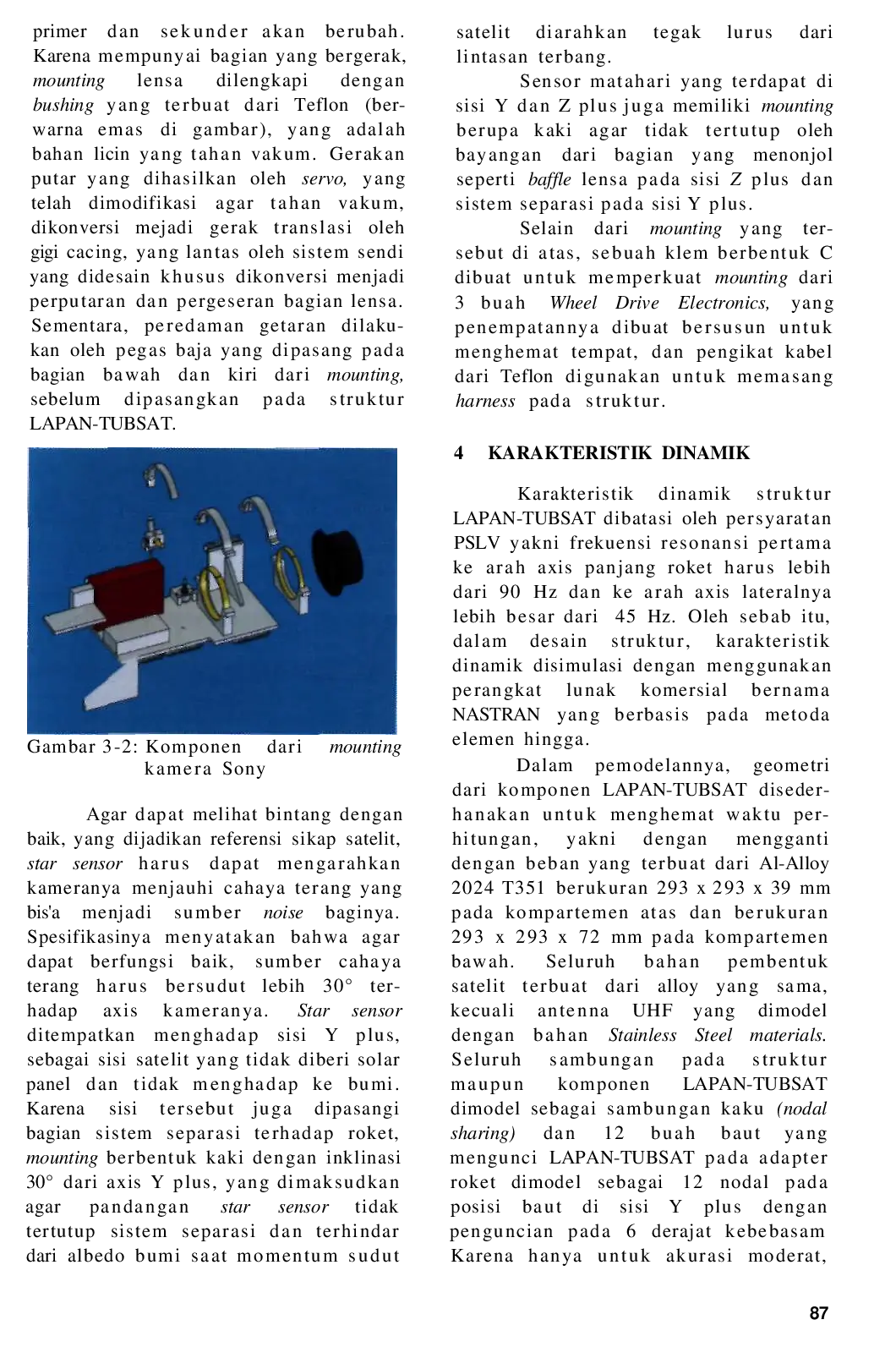
LAPANLAPAN Desain struktur LAPAN-TUBSAT telah memenuhi semua persyaratannya, termasuk optimasi berat, volume, dan inersia sesuai dengan persyaratan peluncuran danDesain struktur LAPAN-TUBSAT telah memenuhi semua persyaratannya, termasuk optimasi berat, volume, dan inersia sesuai dengan persyaratan peluncuran dan