UMJ PremiumUMJ Premium
International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and TechnologyInternational Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and TechnologyWaste oil can be converted to fuel through complex processes due to its high impurity level and significant oxygen content. This research explores the use of pyrolysis together with metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) to enhance the conversion of waste oil. MOFs, porous crystalline materials formed by linking metal ions with organic linkers, provide moderate surface area and increased active sites for catalytic applications, especially in bioproduction. In this study, copper-based MOFs (Cu-MOF) were synthesized via a room temperature method using CuSO4-5H2O and 2-methylimidazole, followed by wet impregnation with K2O. The synthesized catalysts were characterized using FTIR, SEM, and BET and the biofuel production using GC-MS. The characterization results showed that K2O impregnation enhanced the stability of MOF structure and significantly improved thermal stability as well as made it more efficient for the pyrolytic catalytic process for biofuel production. FTIR analysis confirmed the successful impregnation of K2O, SEM analysis showed that the Cu-MOF particles did not have a clear crystal shape. From BET analysis, there is a decrease in surface area due to K2O impregnation. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) confirmed that the pyrolytic reaction occurred by using Cu-MOF/K2O catalyst can significantly increase the hydrocarbon compounds of the waste cooking oil to 39.25% as well as decrease the oxygen content contained in the oil to 56.65% according to the reaction in the pyrolytic catalysis cracking process. Importantly, the catalyst showed regeneration potential after use, proving its feasibility for repeated application in waste oil conversion processes.
This study investigates the conversion of used cooking oil into biofuel using a Cu-MOF/K2O catalyst.The results demonstrate that K2O impregnation successfully enhanced the stability and efficiency of the Cu-MOF catalyst for pyrolytic catalytic cracking.GC-MS analysis confirmed that the Cu-MOF/K2O catalyst significantly increased hydrocarbon production (39.65%) in the biofuel compared to using Cu-MOF alone, indicating its superior performance in waste cooking oil conversion.
Penelitian lebih lanjut perlu dilakukan untuk mengoptimalkan komposisi katalis Cu-MOF/K2O, misalnya dengan memvariasikan rasio K2O terhadap Cu-MOF, guna mencapai aktivitas katalitik yang lebih tinggi dan selektivitas produk yang diinginkan. Selain itu, studi mengenai mekanisme reaksi yang terjadi selama proses pirolisis katalitik dengan menggunakan katalis ini perlu diperdalam, termasuk identifikasi intermediet reaksi dan pengaruhnya terhadap kualitas biofuel yang dihasilkan. Terakhir, penelitian tentang regenerasi dan stabilitas katalis dalam jangka panjang sangat penting untuk memastikan keberlanjutan dan efisiensi ekonomi dari proses konversi minyak goreng bekas menjadi biofuel, termasuk pengujian terhadap berbagai siklus penggunaan katalis dan pengaruhnya terhadap kinerja katalitik.
- 0. loading aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1063/5.01728510 loading aip scitation doi abs 10 1063 5 0172851
- Pembuatan dan Karakterisasi Katalis Nikel/Zeolit pada Pirolisis Tir Batubara | Suyati | Jurnal Kimia... ejournal.undip.ac.id/index.php/ksa/article/view/3306Pembuatan dan Karakterisasi Katalis Nikel Zeolit pada Pirolisis Tir Batubara Suyati Jurnal Kimia ejournal undip ac index php ksa article view 3306
| File size | 331.87 KB |
| Pages | 7 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Evaluation involved 30 Generation Z participants (aged 13-28 years) through pre-test/post-test assessments and usability testing. Results demonstratedEvaluation involved 30 Generation Z participants (aged 13-28 years) through pre-test/post-test assessments and usability testing. Results demonstrated
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM mp4 berdurasi 5 menit yang menjelaskan profil, visi, misi, produk, dan nilai-nilai perusahaan. Video ini lolos pengujian alpha oleh ahli multimedia danmp4 berdurasi 5 menit yang menjelaskan profil, visi, misi, produk, dan nilai-nilai perusahaan. Video ini lolos pengujian alpha oleh ahli multimedia dan
POLKESBANPOLKESBAN Anak-anak dari ibu dengan depresi yang berkelanjutan dilaporkan memiliki risiko hingga enam kali lebih besar mengalami keterlambatan perkembangan emosional,Anak-anak dari ibu dengan depresi yang berkelanjutan dilaporkan memiliki risiko hingga enam kali lebih besar mengalami keterlambatan perkembangan emosional,
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Hasil ini menunjukkan bahwa Flightech Immersion dapat berfungsi sebagai media pendidikan yang inovatif dan efektif untuk mendukung pembelajaran imersifHasil ini menunjukkan bahwa Flightech Immersion dapat berfungsi sebagai media pendidikan yang inovatif dan efektif untuk mendukung pembelajaran imersif
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Penelitian ini menghasilkan motion comic bergaya chibi sebagai media informasi pendaftaran haji. Evaluasi ahli menunjukkan bahwa motion comic ini cukupPenelitian ini menghasilkan motion comic bergaya chibi sebagai media informasi pendaftaran haji. Evaluasi ahli menunjukkan bahwa motion comic ini cukup
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Teknik camera follow menciptakan kesan imersif namun perlu peningkatan dalam menyorot detail koleksi. Rekomendasi untuk penelitian lanjutan meliputi penggunaanTeknik camera follow menciptakan kesan imersif namun perlu peningkatan dalam menyorot detail koleksi. Rekomendasi untuk penelitian lanjutan meliputi penggunaan
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Namun, bukti saat ini masih terbatas oleh metodologi yang lemah, sehingga diperlukan penelitian lebih lanjut untuk memperkuat dampak jangka panjang animasiNamun, bukti saat ini masih terbatas oleh metodologi yang lemah, sehingga diperlukan penelitian lebih lanjut untuk memperkuat dampak jangka panjang animasi
UMSUMS Prediksi iklim dengan rentang 10 tahun, yang dikenal sebagai Prediksi Iklim Dekadal (DCP), telah menjadi aspek penting dalam proyek Coupled Model IntercomparisonPrediksi iklim dengan rentang 10 tahun, yang dikenal sebagai Prediksi Iklim Dekadal (DCP), telah menjadi aspek penting dalam proyek Coupled Model Intercomparison
Useful /
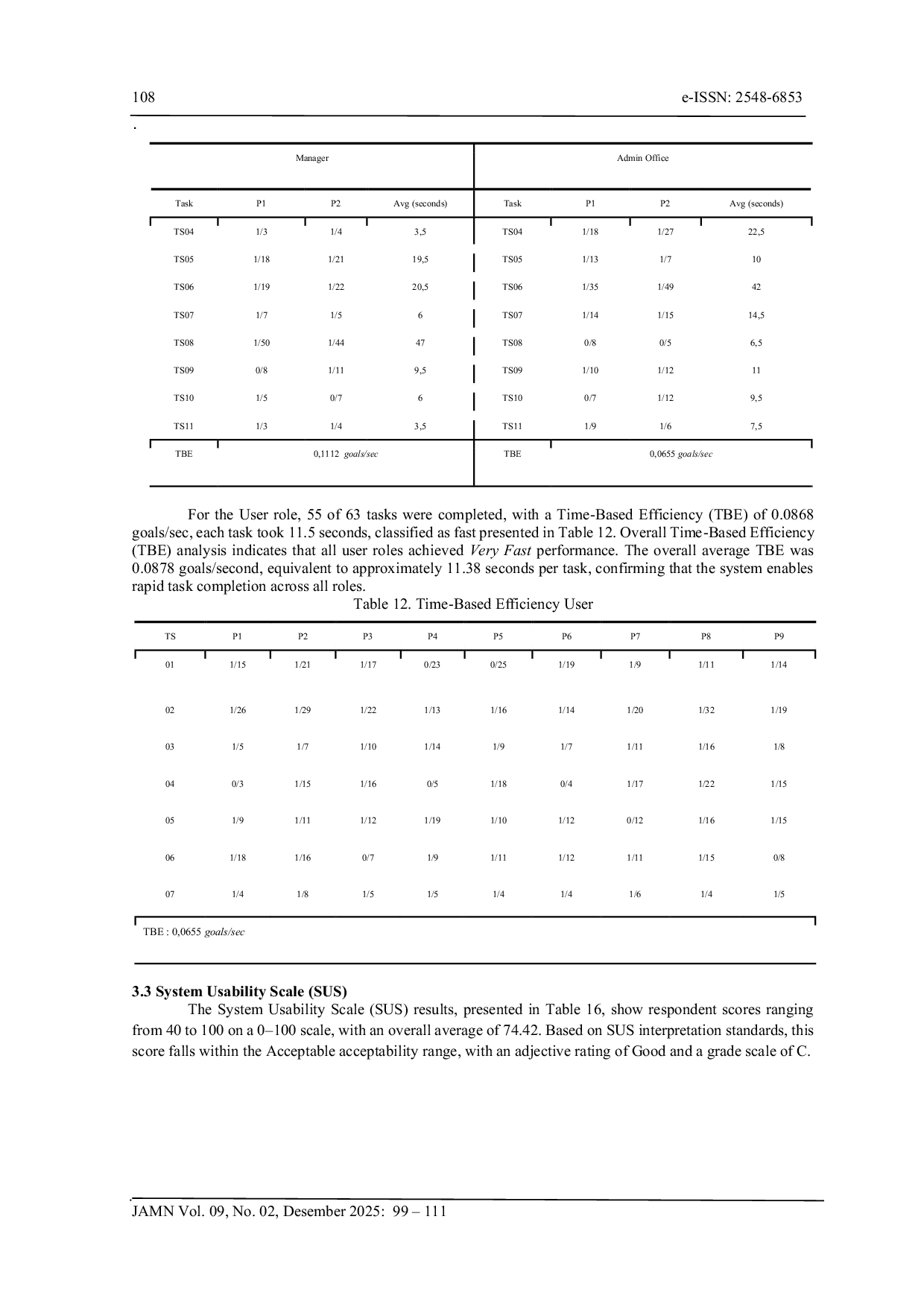
POLIBATAMPOLIBATAM Tingkat Penyelesaian Tugas (TCR) awal sebesar 87,85% menunjukkan bahwa sebagian besar skenario diselesaikan tanpa hambatan besar, dan setelah mengatasiTingkat Penyelesaian Tugas (TCR) awal sebesar 87,85% menunjukkan bahwa sebagian besar skenario diselesaikan tanpa hambatan besar, dan setelah mengatasi
POLKESBANPOLKESBAN Dalam kelompok intervensi dan kontrol, mayoritas responden berusia 17 tahun, memiliki ibu dengan pendidikan SD, memperoleh informasi kesehatan reproduksiDalam kelompok intervensi dan kontrol, mayoritas responden berusia 17 tahun, memiliki ibu dengan pendidikan SD, memperoleh informasi kesehatan reproduksi
POLKESBANPOLKESBAN Penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa deteksi mutasi genetik, khususnya pada HNF1A, penting dalam mendiagnosis MODY secara akurat dan dapat menjadi dasar pemilihanPenelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa deteksi mutasi genetik, khususnya pada HNF1A, penting dalam mendiagnosis MODY secara akurat dan dapat menjadi dasar pemilihan
POLKESBANPOLKESBAN Limbah B3 medis padat dari rumah sakit berpotensi membahayakan kesehatan dan lingkungan jika tidak dikelola dengan baik. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengetahuiLimbah B3 medis padat dari rumah sakit berpotensi membahayakan kesehatan dan lingkungan jika tidak dikelola dengan baik. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengetahui