PDSIPDSI
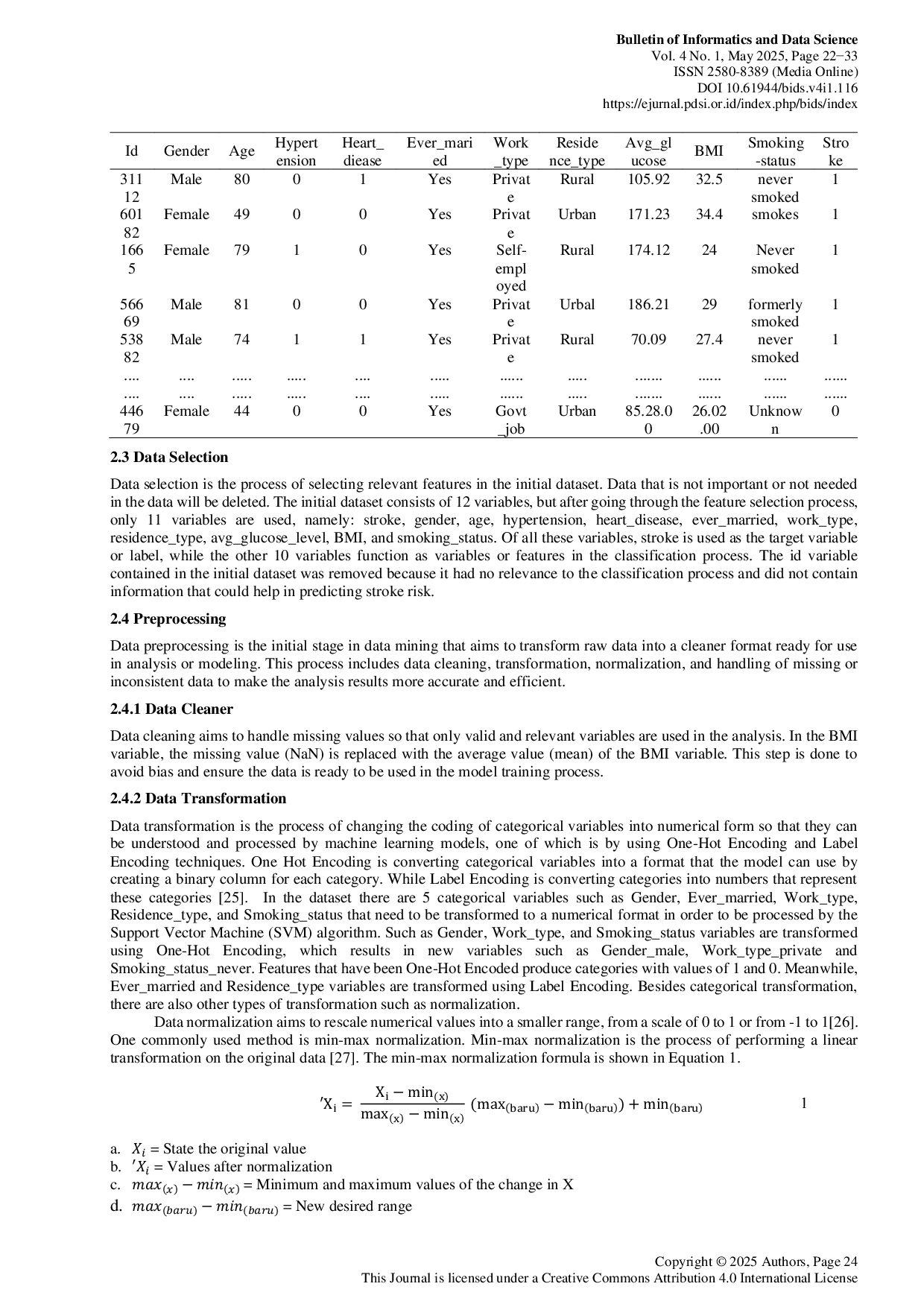
Bulletin of Informatics and Data ScienceBulletin of Informatics and Data ScienceDiabetes is a major cause of many chronic diseases such as visual impairment, stroke and kidney failure. Early detection especially in groups that have a high risk of developing diabetes needs to be done to prevent problems that have a wide impact. Indonesia is ranked seventh in the world with a prevalence of 10.7% of the total number of people with diabetes. This research aims to determine the attributes in the diabetes dataset that most affect the classification and apply the Support Vector Machine method for diabetes classification. For the determination process, Gain Ratio feature selection technique is applied. The dataset used consists of 768 data with 8 attributes. In this classification process, 3 SVM kernels (Linear, Polynomial, and RBF) are used with three possible data divisions using the ratio (70:30; 80:20; 90:10). Before applying feature selection, there were 8 attributes used and achieved the highest accuracy of 94.81% at a ratio of 80:20 using the RBF kernel with a combination of two parameters namely C = 100, Gamma = 3 and C = 100, Gamma = Scale. Feature selection parameters in the form of thresholds used include 0.02; 0.03; and 0.05. After applying feature selection, the attribute that produces the highest accuracy uses 6 attributes. The highest accuracy after applying feature selection reached 95.45% at a threshold of 0.02 with a ratio of 80:20 using the RBF kernel with parameters C = 100 and Gamma = Scale. The results showed that there was an increase in accuracy after applying feature selection.
The application of the Gain Ratio feature selection in the Support Vector Machine method successfully increased the accuracy of diabetes classification by 0.20 data ratio, and the RBF kernel with parameters C = 100 and Gamma = Scale.The RBF kernel consistently demonstrated optimal performance.The right combination of threshold, data ratio, and kernel parameters can produce a more reliable model for predicting diabetes risk.
Penelitian lebih lanjut dapat dilakukan dengan mengeksplorasi teknik data balancing untuk mengatasi ketidakseimbangan jumlah data antara kelas diabetes dan non-diabetes, karena hal ini berpotensi meningkatkan kinerja model klasifikasi. Selain itu, penelitian dapat diperluas dengan menguji kombinasi parameter yang lebih beragam pada algoritma SVM, termasuk penggunaan teknik optimasi parameter otomatis untuk menemukan konfigurasi terbaik. Sebagai pengembangan, studi komparatif dapat dilakukan dengan menerapkan teknik seleksi fitur Gain Ratio pada algoritma machine learning lainnya, seperti Random Forest atau Decision Tree, untuk mengidentifikasi algoritma mana yang paling efektif dalam memprediksi risiko diabetes. Penelitian ini juga dapat diperkaya dengan mempertimbangkan faktor-faktor lain yang mungkin mempengaruhi risiko diabetes, seperti data gaya hidup, riwayat keluarga, atau informasi genetik, untuk membangun model prediksi yang lebih komprehensif dan akurat. Terakhir, validasi model pada dataset yang lebih besar dan beragam dari berbagai populasi dapat dilakukan untuk memastikan generalisasi dan keandalan model dalam aplikasi dunia nyata.
- Komparasi Information Gain, Gain Ratio, CFs-Bestfirst dan CFs-PSO Search Terhadap Performa Deteksi Anomali... ejurnal.stmik-budidarma.ac.id/index.php/mib/article/view/2258Komparasi Information Gain Gain Ratio CFs Bestfirst dan CFs PSO Search Terhadap Performa Deteksi Anomali ejurnal stmik budidarma ac index php mib article view 2258
- Performance Analysis of LVQ 1 Using Feature Selection Gain Ratio for Sex Classification in Forensic Anthropology... ejurnal.seminar-id.com/index.php/bits/article/view/3625Performance Analysis of LVQ 1 Using Feature Selection Gain Ratio for Sex Classification in Forensic Anthropology ejurnal seminar id index php bits article view 3625
| File size | 706.23 KB |
| Pages | 12 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
IVETIVET Pengelolaan air bersih di instansi pemerintahan sering kali bergantung pada mekanisme manual atau saklar pelampung yang kurang efisien, menyebabkan pemborosanPengelolaan air bersih di instansi pemerintahan sering kali bergantung pada mekanisme manual atau saklar pelampung yang kurang efisien, menyebabkan pemborosan
AHMARAHMAR (1) Peramalan menggunakan metode Support Vector Regression (SVR) menghasilkan model terbaik dengan kernel radial, menggunakan parameter ε=0,1, C=100,(1) Peramalan menggunakan metode Support Vector Regression (SVR) menghasilkan model terbaik dengan kernel radial, menggunakan parameter ε=0,1, C=100,
KIPMIKIPMI Hasil ini menggarisbawahi pentingnya metilasi DNA yang dimediasi DNMT dalam adipogenesis dan kanker payudara. Studi ini menyajikan analisis komprehensifHasil ini menggarisbawahi pentingnya metilasi DNA yang dimediasi DNMT dalam adipogenesis dan kanker payudara. Studi ini menyajikan analisis komprehensif
STMIKJAYAKARTASTMIKJAYAKARTA 46398 untuk produk brownies, k = 9 menghasilkan nilai RMSE 0. 46827 untuk produk coklat, k = 14 menghasilkan nilai RMSE 0. 47980 untuk produk Donat, k46398 untuk produk brownies, k = 9 menghasilkan nilai RMSE 0. 46827 untuk produk coklat, k = 14 menghasilkan nilai RMSE 0. 47980 untuk produk Donat, k
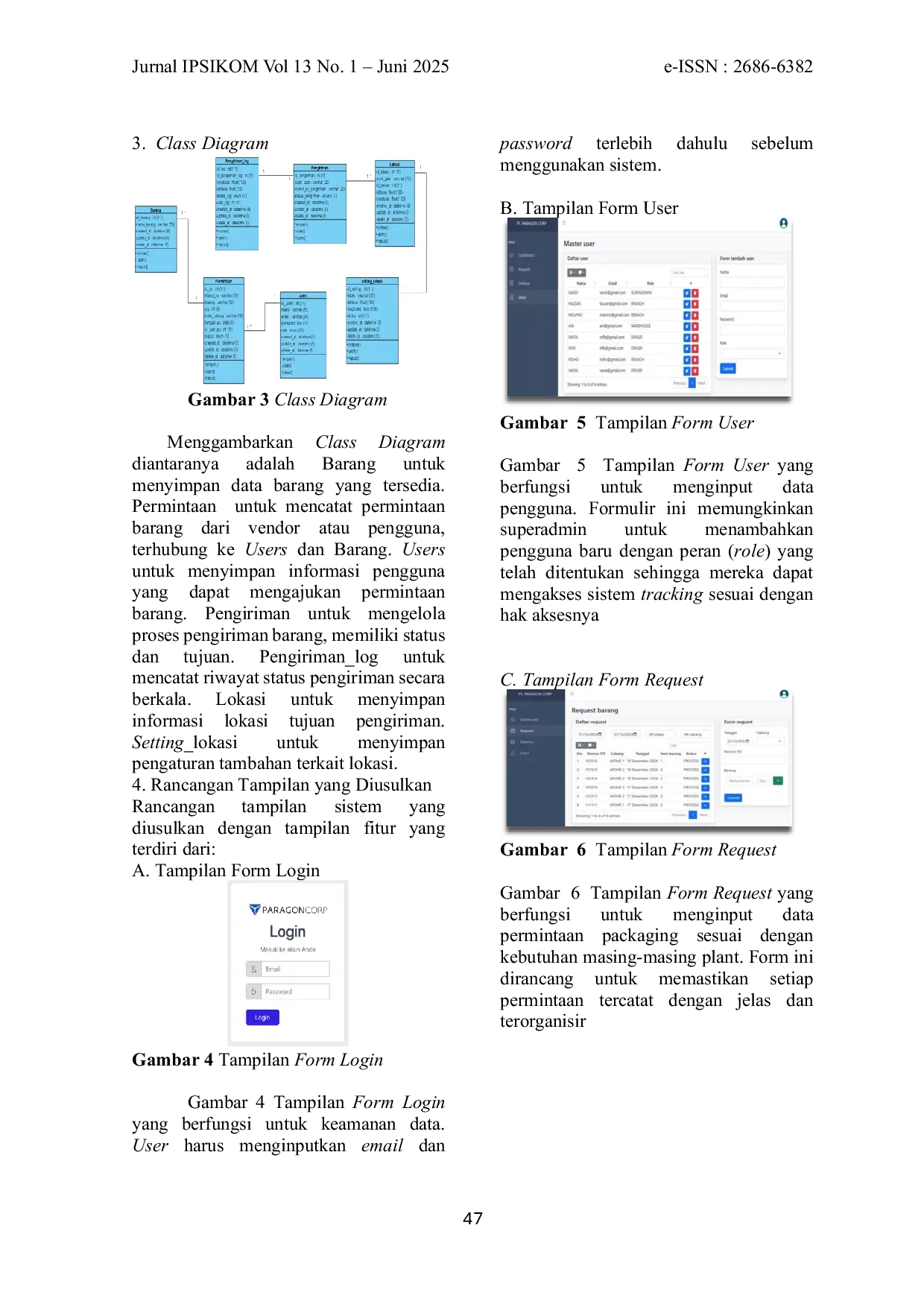
UNIPEMUNIPEM Sistem tracking dibangun untuk mengatasi permasalahan yang terjadi pada PT. XYZ dalam hal rantai pasok distribusi barang kemasan dimana kurangnya pengawasanSistem tracking dibangun untuk mengatasi permasalahan yang terjadi pada PT. XYZ dalam hal rantai pasok distribusi barang kemasan dimana kurangnya pengawasan
PDSIPDSI Oleh karena itu, metode prediksi berbasis data yang menggunakan pembelajaran mesin telah muncul sebagai alternatif yang menjanjikan untuk mendukung identifikasiOleh karena itu, metode prediksi berbasis data yang menggunakan pembelajaran mesin telah muncul sebagai alternatif yang menjanjikan untuk mendukung identifikasi
PDSIPDSI Metode konvensional seperti analisis DNA sering digunakan, tetapi memiliki keterbatasan, terutama ketika tulang rusak, hangus, atau membusuk, sehinggaMetode konvensional seperti analisis DNA sering digunakan, tetapi memiliki keterbatasan, terutama ketika tulang rusak, hangus, atau membusuk, sehingga
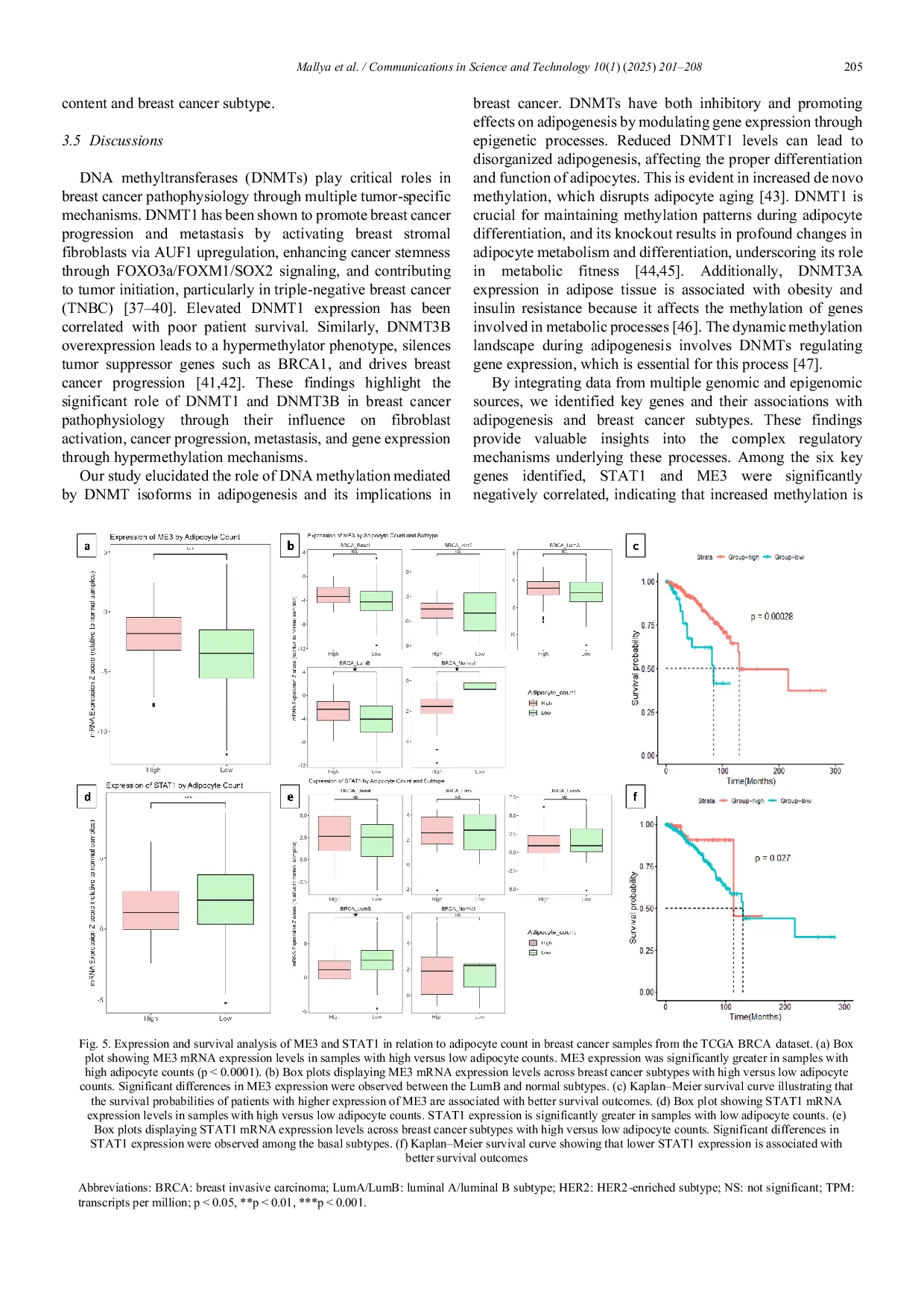
PDSIPDSI These results show that the combination of techniques used aims to determine the variables that most affect SVM classification in detecting stroke disease.These results show that the combination of techniques used aims to determine the variables that most affect SVM classification in detecting stroke disease.
Useful /
WIDYADHARMAWIDYADHARMA Pembelajaran online telah menjadi metode pengajaran yang umum selama pandemi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui sikap mahasiswa terhadap mata kuliahPembelajaran online telah menjadi metode pengajaran yang umum selama pandemi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui sikap mahasiswa terhadap mata kuliah
UNDAUNDA Label Syariah tidak berpengaruh terhadap keputusan investor dalam berinvestasi saham. Label syariah akan lebih kuat mempengaruhi keputusan investasi jikaLabel Syariah tidak berpengaruh terhadap keputusan investor dalam berinvestasi saham. Label syariah akan lebih kuat mempengaruhi keputusan investasi jika
UNIBUNIB The outcomes are interactive multimedia using Moodle and ThingLink, complete with its tutorials, practices, and tests to listening comprehension. InteractiveThe outcomes are interactive multimedia using Moodle and ThingLink, complete with its tutorials, practices, and tests to listening comprehension. Interactive
UNIBUNIB Dua puluh tiga mahasiswa menyatakan setuju sekali dan tujuh mahasiswa menyatakan setuju terhadap indikator pembelajaran. Untuk indikator materi, dua belasDua puluh tiga mahasiswa menyatakan setuju sekali dan tujuh mahasiswa menyatakan setuju terhadap indikator pembelajaran. Untuk indikator materi, dua belas