STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI
JKBLJKBLHyperemesis gravidarum is a condition characterized by excessive vomiting, which may lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, acid-base disturbances, and significant weight loss in pregnant women. Management of hyperemesis gravidarum requires controlling nausea and vomiting to prevent active fluid loss. One potential complementary intervention is the use of Zingiber officinale (ginger) herbal therapy. This study aims to describe complementary nursing care focused on managing hypovolemia in a patient with hyperemesis gravidarum through the use of Zingiber officinale herbal therapy. The research employed a descriptive case study design to identify nursing care problems in a patient diagnosed with hyperemesis gravidarum. The subject was Mrs. S, a G1P0A0H0 patient at 9 weeks of gestation. The identified nursing diagnosis was hypovolemia related to active fluid loss, evidenced by nausea and vomiting more than five times per day, weakness, dizziness, dry lip mucosa, capillary refill time (CRT) > 2 seconds, urine ketones 3 , and decreased blood pressure (100/60 mmHg). The nursing intervention focused on managing hypovolemia and reducing nausea and vomiting through the administration of Zingiber officinale herbal therapy twice daily. After 72 hours (3×24 hours) of nursing care, the evaluation showed improvement in the patients condition: no more vomiting or dizziness, CRT < 2 seconds, moist mucous membranes, negative urine ketones, improved fluid intake, and stable blood pressure (110/70 mmHg). This study concludes that Zingiber officinale herbal therapy is effective in reducing nausea and vomiting and may help prevent potential complications during pregnancy.
S, focused on managing hypovolemia caused by hyperemesis gravidarum, demonstrated positive outcomes.Interventions combining isotonic fluid administration and ginger herbal therapy, given twice daily for three days, led to improvements such as decreased nausea and vomiting, increased lip mucosa moisture, and stabilized blood pressure and fluid intake.These findings suggest that this combined approach has the potential to reduce nausea and vomiting and prevent fluid loss associated with hypovolemia.
Further research is needed to confirm the effectiveness and safety of Zingiber officinale herbal therapy for hyperemesis gravidarum, considering the limitations of this case study. Future studies should investigate the optimal dosage and duration of ginger administration to maximize its therapeutic benefits and minimize potential side effects. Additionally, research could explore the underlying mechanisms by which ginger alleviates nausea and vomiting during pregnancy, potentially identifying specific biochemical pathways involved. Investigating the impact of ginger therapy on fetal well-being, including growth and development, is also crucial. Finally, studies comparing the efficacy of ginger therapy to conventional antiemetic medications, and exploring its potential as a complementary therapy alongside standard care, would provide valuable insights for clinical practice. These investigations should involve larger, more diverse patient populations and employ rigorous research methodologies to ensure reliable and generalizable results, ultimately contributing to improved care for pregnant women experiencing hyperemesis gravidarum.
- The hyperemesis gravidarum and pulmonary embolism: A case report and review of literature | QScience.com.... doi.org/10.5339/qmj.2024.39The hyperemesis gravidarum and pulmonary embolism A case report and review of literature QScience doi 10 5339 qmj 2024 39
- PENGARUH PEMBERIAN SEDUHAN JAHE (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE VAR. AMARUM) TERHADAP TINGKAT EMESIS GRAVIDARUM... journal.universitaspahlawan.ac.id/index.php/jkt/article/view/18918PENGARUH PEMBERIAN SEDUHAN JAHE ZINGIBER OFFICINALE VAR AMARUM TERHADAP TINGKAT EMESIS GRAVIDARUM journal universitaspahlawan ac index php jkt article view 18918
- The effectzingiber officinale PENGARUH AIR SEDUHAN JAHE (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE) TERHADAP PENURUNAN MUAL... Doi.Org/10.30604/Jaman.V3i2.472The effectzingiber officinale PENGARUH AIR SEDUHAN JAHE ZINGIBER OFFICINALE TERHADAP PENURUNAN MUAL Doi Org 10 30604 Jaman V3i2 472
| File size | 193.32 KB |
| Pages | 5 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Kesimpulan: MMT secara efektif meningkatkan kekuatan otot ekstremitas atas pada pasien stroke non‑hemoragik ini, sehingga profesional kesehatan dapatKesimpulan: MMT secara efektif meningkatkan kekuatan otot ekstremitas atas pada pasien stroke non‑hemoragik ini, sehingga profesional kesehatan dapat
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Sampel penelitian terdiri dari 100 responden yang dipilih dengan teknik purposif acak sederhana. Data dikumpulkan melalui kuesioner yang mengukur variabelSampel penelitian terdiri dari 100 responden yang dipilih dengan teknik purposif acak sederhana. Data dikumpulkan melalui kuesioner yang mengukur variabel
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Desain studi kasus deskriptif digunakan untuk mengidentifikasi masalah keperawatan. Subjek penelitian ini adalah Bayi J. Diagnosis keperawatan yang ditetapkanDesain studi kasus deskriptif digunakan untuk mengidentifikasi masalah keperawatan. Subjek penelitian ini adalah Bayi J. Diagnosis keperawatan yang ditetapkan
PANCABHAKTIPANCABHAKTI Penerimaan diri adalah kemampuan individu untuk menerima kekurangan dan kesalahan, rasa malu yang menghancurkan dan kecemasan yang ekstrem. PenelitianPenerimaan diri adalah kemampuan individu untuk menerima kekurangan dan kesalahan, rasa malu yang menghancurkan dan kecemasan yang ekstrem. Penelitian
STIKESPANTIWALUYASTIKESPANTIWALUYA Manifestasi klinis penyakit dan proses pengobatan OAT yang panjang dan intensif, dapat berkembang menjadi sumber stresor yang dapat berkembang menjadiManifestasi klinis penyakit dan proses pengobatan OAT yang panjang dan intensif, dapat berkembang menjadi sumber stresor yang dapat berkembang menjadi
POLTEKKESKUPANGPOLTEKKESKUPANG The exercise program (Tai Chi Gymnastics and Cognitive Stimulation) has been proven to effectively improve the health status of the elderly. This programThe exercise program (Tai Chi Gymnastics and Cognitive Stimulation) has been proven to effectively improve the health status of the elderly. This program
STIKESPANTIWALUYASTIKESPANTIWALUYA Latar Belakang: Daya tahan tubuh berperan dalam melindungi tubuh saat kuman pertama kali masuk ke dalam tubuh, oleh karena itu harus senantiasa dijagaLatar Belakang: Daya tahan tubuh berperan dalam melindungi tubuh saat kuman pertama kali masuk ke dalam tubuh, oleh karena itu harus senantiasa dijaga
POLANKAPOLANKA Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah metode deskriptif dengan pendekatan kuantitatif. Rancangan penelitian yang digunakan yaitu rancanganMetode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah metode deskriptif dengan pendekatan kuantitatif. Rancangan penelitian yang digunakan yaitu rancangan
Useful /
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Langkah-langkah praktis dapat mencakup implementasi atau peningkatan program pendidikan fisik di sekolah, mempromosikan olahraga ekstrakurikuler, mendorongLangkah-langkah praktis dapat mencakup implementasi atau peningkatan program pendidikan fisik di sekolah, mempromosikan olahraga ekstrakurikuler, mendorong
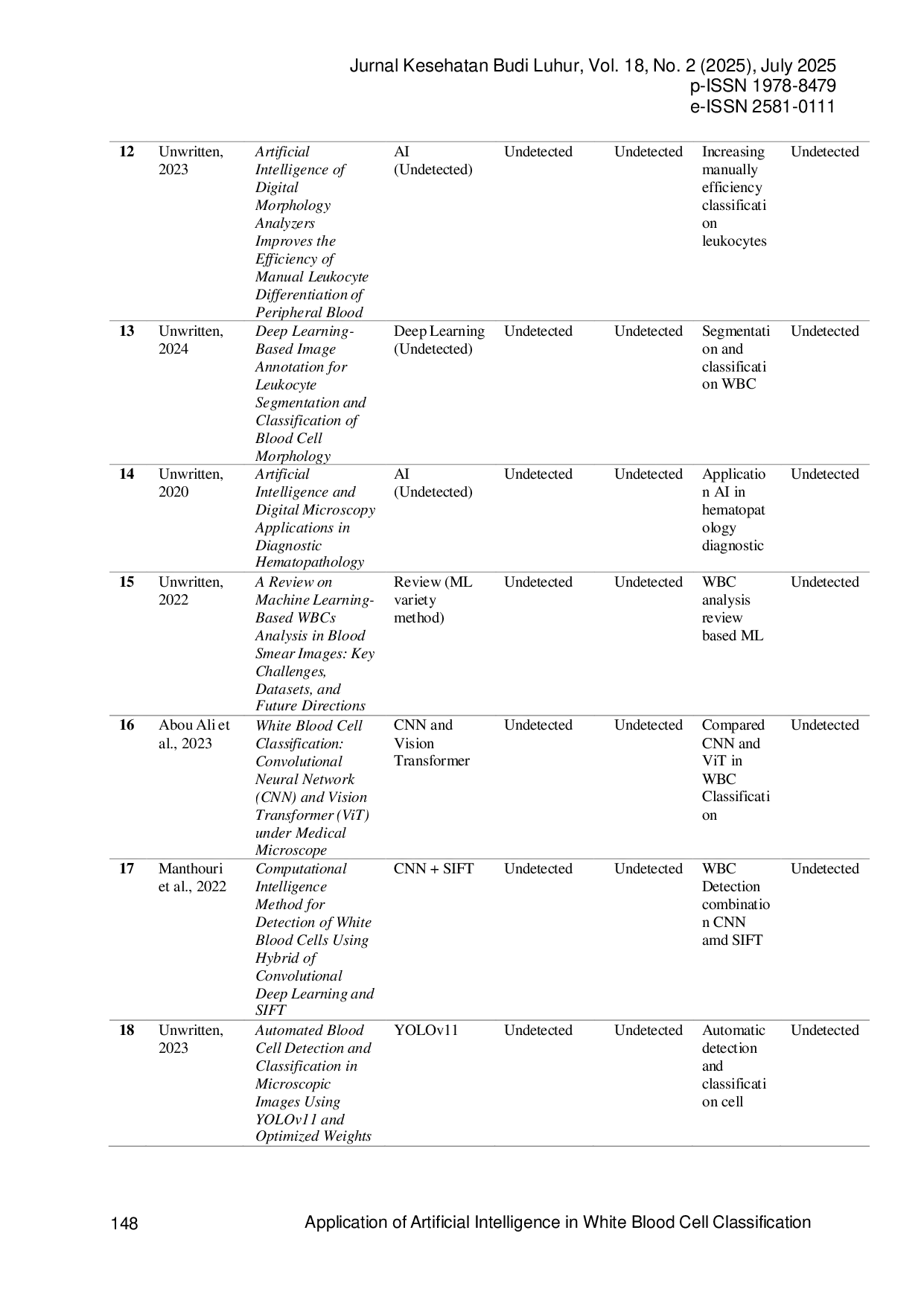
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI Despite encouraging outcomes, challenges such as external validation and limited access to real clinical data remain. Overall, AI has proven effectiveDespite encouraging outcomes, challenges such as external validation and limited access to real clinical data remain. Overall, AI has proven effective
STIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHISTIKESBUDILUHURCIMAHI This indicates a positive influence of the application on the knowledge of women of childbearing age regarding contraceptive choices. Therefore, the WHOThis indicates a positive influence of the application on the knowledge of women of childbearing age regarding contraceptive choices. Therefore, the WHO
ALIMSPUBLISHINGALIMSPUBLISHING Lagu bergenre indie ini disukai banyak khalayak ramai karena bahasa yang digunakan enak didengar juga ramah di telinga karena bahasa yang digunakan sangatLagu bergenre indie ini disukai banyak khalayak ramai karena bahasa yang digunakan enak didengar juga ramah di telinga karena bahasa yang digunakan sangat