IAESONLINEIAESONLINE
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI)Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI)This article introduces a novel blind image quality metric (BIQM) for color images which is designed taking into account human visual system characteristics. The BIQM has a four-stage framework: RGB to YUV transformation, denoising with convolutional neural network , quality evaluation, and weighting to make it compatible with the human visual system. Experimental results, including Spearmans rank-order correlation coefficient, confirm BIQMs effectiveness, particularly in scenarios involving white noise and its compatibility with the human visual system. Furthermore, a survey involving 100 participants ranks images based on three distinct qualities, validating the methods alignment with the human visual system. The comparative analysis reveals that the proposed BIQM can compete with commonly used non-referenced quality measures and is more accurate than some of them. The MATLAB codes for the development of the BIQM are made available through the provided link: https://bit.ly/49MrbFX.
This study proposes a new deep CNN-based NR image quality metric (BIQM) consisting of four phases, including RGB to YUV transform, CNN determination considering the file type, denoising with deep-CNN, and quality value calculation.The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the presented method, particularly for white noise.The SROCC values indicate that BIQM provides more consistent results in terms of HVS compared to its counterparts, particularly for images corrupted with white noise.Moreover, the survey results suggest that BIQM could potentially enhance user satisfaction when used for image quality measurement.The main contribution of this work is the integration of DnCNN residual learning with HVS-based channel weighting.This combination improves the robustness of BIQM against various distortions.
Berdasarkan latar belakang, metode, hasil, keterbatasan, dan saran penelitian lanjutan yang ada dalam paper, berikut adalah beberapa saran penelitian lanjutan yang dapat dikembangkan:. . 1. **Pengembangan Model CNN yang Lebih Adaptif:** Penelitian selanjutnya dapat difokuskan pada pengembangan model CNN yang lebih adaptif terhadap berbagai jenis noise dan distorsi gambar. Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan menggunakan teknik pembelajaran transfer (transfer learning) atau dengan melatih model pada dataset yang lebih beragam dan representatif.. 2. **Integrasi dengan Model Perseptual yang Lebih Kompleks:** BIQM saat ini menggunakan weighting sederhana berdasarkan rasio sel cahaya dan warna pada retina. Penelitian selanjutnya dapat mengeksplorasi integrasi dengan model perceptual yang lebih kompleks, seperti model yang mempertimbangkan efek psikovisual lainnya, untuk meningkatkan akurasi dan kesesuaian dengan persepsi manusia.. 3. **Evaluasi pada Aplikasi Real-World:** Meskipun BIQM telah dievaluasi pada berbagai dataset standar, evaluasi lebih lanjut pada aplikasi real-world, seperti sistem pengawasan video atau aplikasi medis, akan memberikan wawasan yang lebih berharga tentang kinerja dan keandalan BIQM dalam kondisi praktis.
| File size | 1.45 MB |
| Pages | 16 |
| Short Link | https://juris.id/p-3qB |
| Lookup Links | Google ScholarGoogle Scholar, Semantic ScholarSemantic Scholar, CORE.ac.ukCORE.ac.uk, WorldcatWorldcat, ZenodoZenodo, Research GateResearch Gate, Academia.eduAcademia.edu, OpenAlexOpenAlex, Hollis HarvardHollis Harvard |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
UBHINUSUBHINUS Sistem ini dirancang untuk membantu petani ikan dalam menentukan parameter kualitas air yang optimal, seperti suhu, ph, kadar oksigen terlarut, dan kekeruhan,Sistem ini dirancang untuk membantu petani ikan dalam menentukan parameter kualitas air yang optimal, seperti suhu, ph, kadar oksigen terlarut, dan kekeruhan,
UNIPEMUNIPEM Penelitian ini bertujuan mengimplementasi dan mengembangkan SIREJU (Sistem Rekomendasi Jurusan), sebuah Decision Support System (DSS) berbasis rule-basedPenelitian ini bertujuan mengimplementasi dan mengembangkan SIREJU (Sistem Rekomendasi Jurusan), sebuah Decision Support System (DSS) berbasis rule-based
ITSITS Penelitian ini menyelidiki penerapan model deteksi kegagalan berdasarkan pendekatan pembelajaran mesin dan statistik untuk mengurangi waktu henti yangPenelitian ini menyelidiki penerapan model deteksi kegagalan berdasarkan pendekatan pembelajaran mesin dan statistik untuk mengurangi waktu henti yang
UBHARAUBHARA Meski penggunaan machine learning dalam deteksi kesehatan mental meningkat, penelitian tentang penanganan dataset tidak seimbang di populasi mahasiswaMeski penggunaan machine learning dalam deteksi kesehatan mental meningkat, penelitian tentang penanganan dataset tidak seimbang di populasi mahasiswa
UBHINUSUBHINUS Sistem yang dikembangkan diharapkan dapat memberikan rekomendasi motor matic yang sesuai dengan preferensi dan kebutuhan pengguna. Tantangan dalam memilihSistem yang dikembangkan diharapkan dapat memberikan rekomendasi motor matic yang sesuai dengan preferensi dan kebutuhan pengguna. Tantangan dalam memilih
UBHINUSUBHINUS Metode yang digunakan adalah Rapid Application Development (RAD) yang terdiri dari empat tahap: perencanaan kebutuhan, desain pengguna, konstruksi, danMetode yang digunakan adalah Rapid Application Development (RAD) yang terdiri dari empat tahap: perencanaan kebutuhan, desain pengguna, konstruksi, dan
STMISTMI Penggunaan metode pengembangan sistem yang dipilih adalah waterfall untuk dapat membantu dalam melakukan pengembangan sistem informasi berbasis ObjectPenggunaan metode pengembangan sistem yang dipilih adalah waterfall untuk dapat membantu dalam melakukan pengembangan sistem informasi berbasis Object
ITKITK Tiga atribut yang paling berpengaruh dalam membangun model prediksi saldo produksi hasil ternak adalah komoditas, nilai produksi, dan biaya produksi (Rp),Tiga atribut yang paling berpengaruh dalam membangun model prediksi saldo produksi hasil ternak adalah komoditas, nilai produksi, dan biaya produksi (Rp),
Useful /
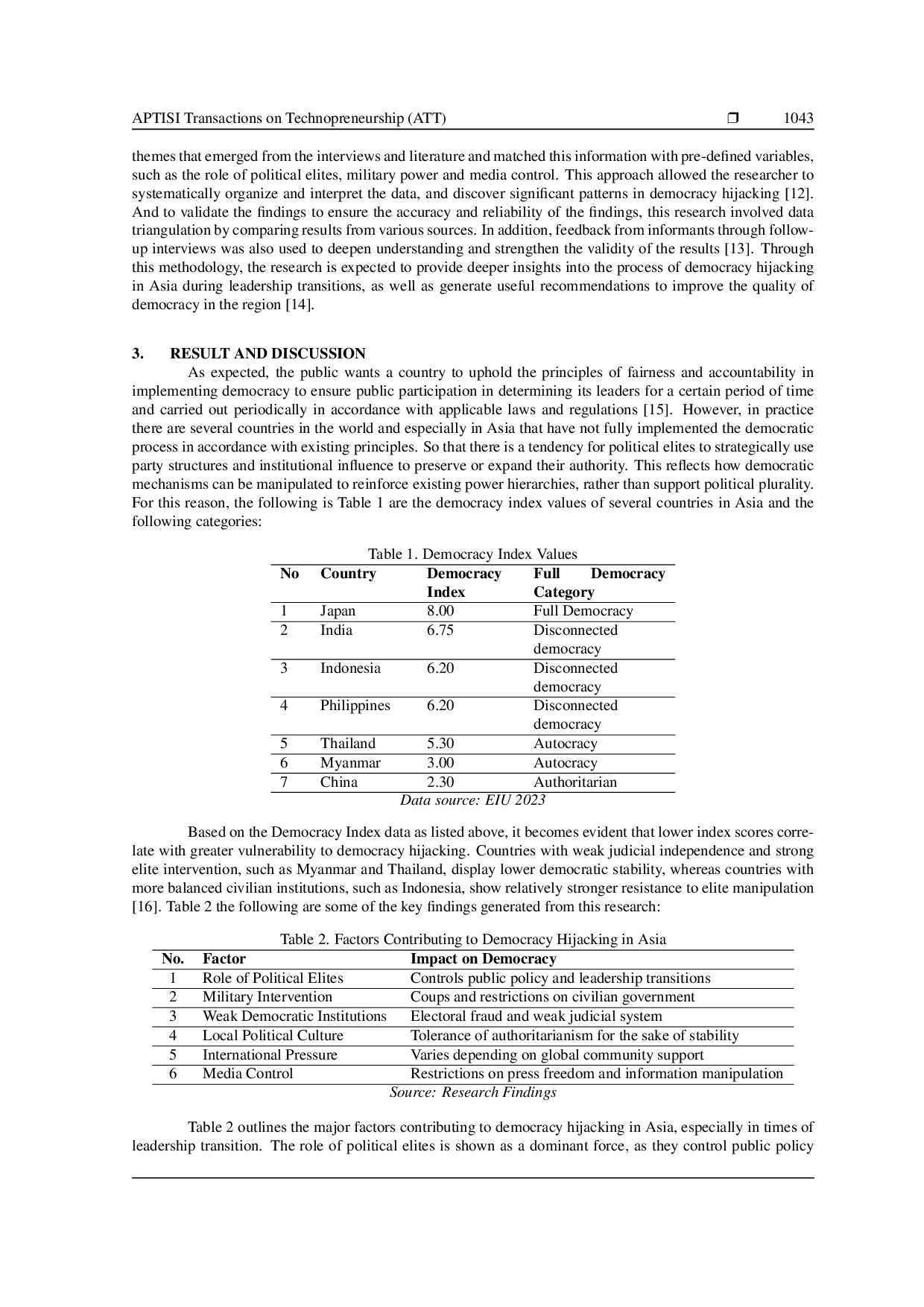
APTISIAPTISI Isu ini sepenuhnya berhubungan dengan SDGs 16: Damai, Kekuatan Hakim, dan Institusi yang Kuat, yang menekankan tata kelola yang terbuka, partisipasi politik,Isu ini sepenuhnya berhubungan dengan SDGs 16: Damai, Kekuatan Hakim, dan Institusi yang Kuat, yang menekankan tata kelola yang terbuka, partisipasi politik,
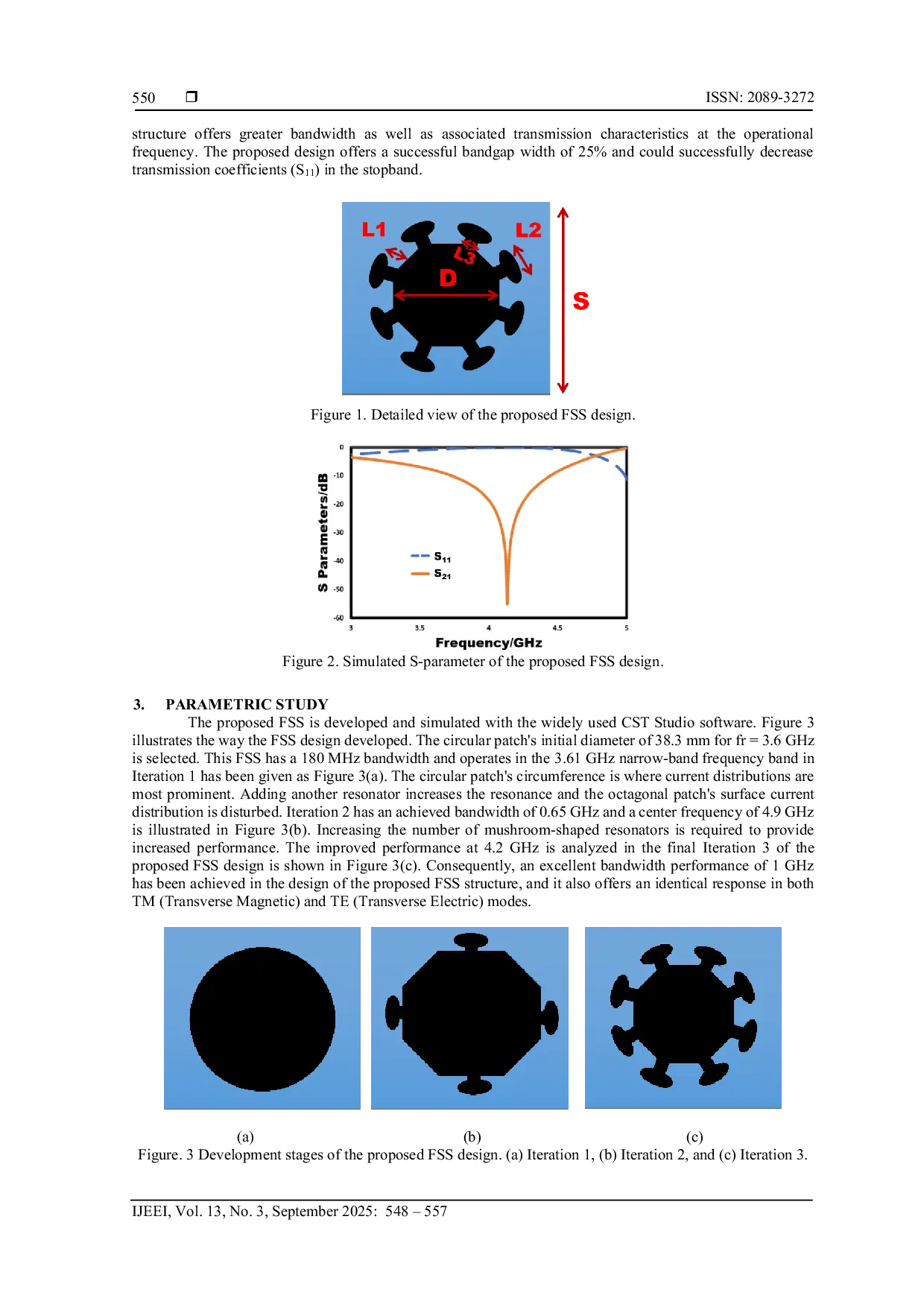
IAESONLINEIAESONLINE The proposed modified octagonal-shaped FSS demonstrates strong performance for 5G communication at frequencies below 6 GHz. The compact size, angular stabilityThe proposed modified octagonal-shaped FSS demonstrates strong performance for 5G communication at frequencies below 6 GHz. The compact size, angular stability
IAESONLINEIAESONLINE 0%, and recall of 96. 0%, along with an F1 measure of 96. 0%. The result of the experiment indicates that the model is effective and, when implemented,0%, and recall of 96. 0%, along with an F1 measure of 96. 0%. The result of the experiment indicates that the model is effective and, when implemented,
STMISTMI PT Autoplastik Indonesia, anak perusahaan PT Astra Otoparts Tbk, bergerak dalam produksi komponen plastik untuk kendaraan roda empat. Mereka menghasilkanPT Autoplastik Indonesia, anak perusahaan PT Astra Otoparts Tbk, bergerak dalam produksi komponen plastik untuk kendaraan roda empat. Mereka menghasilkan