JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD
Jurnal Akademika KimiaJurnal Akademika KimiaThis study discusses the implementation of redox reactions on the thickness test of the galvanized (zinc-coated) layer using the JIS-H-0401 standard to help Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) industries. Some of the finished products go through the galvanizing process in the metal processing industry. Quality constraints, especially related to the thickness of the galvanic (zinc-coated) layer, have become an object that is less controlled because of the limitations of the test equipment used. This research uses an experimental method applied to one of its products: a flat washer with SPCC material and a thickness of about 2.20 mm. SPCC - SD material is classified as low carbon steel based on its carbon content. 5-unit flat washers were identified with sample codes A, B, C, D, and E. Flat washers have an internal diameter of 22.65 - 22.7 mm. In comparison, the outer diameter is between 43.75 - 43.80. The redox reaction process used HCl (hydrochloric acid) with a concentration of 1 M, which was diluted with water (H2O). The zinc thickness test results showed that the flat washer has an average thickness of 10.52 microns with a minimum and maximum thickness variation of 10.66 -10.72 microns.
The redox reaction was successfully conducted to evaluate the zinc thickness testing process with a 1.0 M hydrochloric acid solution diluted to 0.The thickness of the zinc layer was measured to be 10.Regarding quality, the galvanizing process results produced by SMEs are still below the general standard for component binders.
Further research should investigate the influence of varying hydrochloric acid concentrations on the accuracy and efficiency of the zinc thickness testing method, potentially optimizing the process for wider SME adoption. Additionally, exploring the correlation between the surface roughness of the galvanized material and the results obtained from the redox reaction test could enhance the reliability of quality control. Finally, a comparative study evaluating the cost-effectiveness of this redox reaction method against existing zinc thickness testing techniques would provide valuable insights for SMEs seeking affordable quality assurance solutions, ultimately contributing to improved product competitiveness and adherence to industry standards. These investigations should consider the practical limitations of SMEs, focusing on simplicity and accessibility of implementation.
| File size | 253.46 KB |
| Pages | 7 |
| DMCA | ReportReport |
Related /
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD Development of the learning module is expected to be used by teachers as users and for students in their independent learning, increasing the understandingDevelopment of the learning module is expected to be used by teachers as users and for students in their independent learning, increasing the understanding
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD ) Griff. ) berpotensi sebagai tabir surya. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengidentifikasi isolat senyawa flavonoid dari daun wungu dan menentukan nilai SPF.) Griff. ) berpotensi sebagai tabir surya. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengidentifikasi isolat senyawa flavonoid dari daun wungu dan menentukan nilai SPF.
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD Hasil karakterisasi XRD dan FTIR menunjukkan bahwa karbon aktif yang diperoleh memiliki struktur amorf dan karbon aktif yang diperoleh memiliki kelompokHasil karakterisasi XRD dan FTIR menunjukkan bahwa karbon aktif yang diperoleh memiliki struktur amorf dan karbon aktif yang diperoleh memiliki kelompok
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD Nilai IC50 ekstrak etanol kulit buah kakao masak dan muda (Theobroma Cacao L. ) berturut-turut adalah 76,094 ppm dan 91,884 ppm. Kulit buah kakao masakNilai IC50 ekstrak etanol kulit buah kakao masak dan muda (Theobroma Cacao L. ) berturut-turut adalah 76,094 ppm dan 91,884 ppm. Kulit buah kakao masak
Useful /
STTSIMPSONSTTSIMPSON Penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa tradisi Bada mengandung nilai-nilai dan struktur etis yang selaras dengan ajaran-ajaran biblis, dan dapat dijadikan sebagaiPenelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa tradisi Bada mengandung nilai-nilai dan struktur etis yang selaras dengan ajaran-ajaran biblis, dan dapat dijadikan sebagai
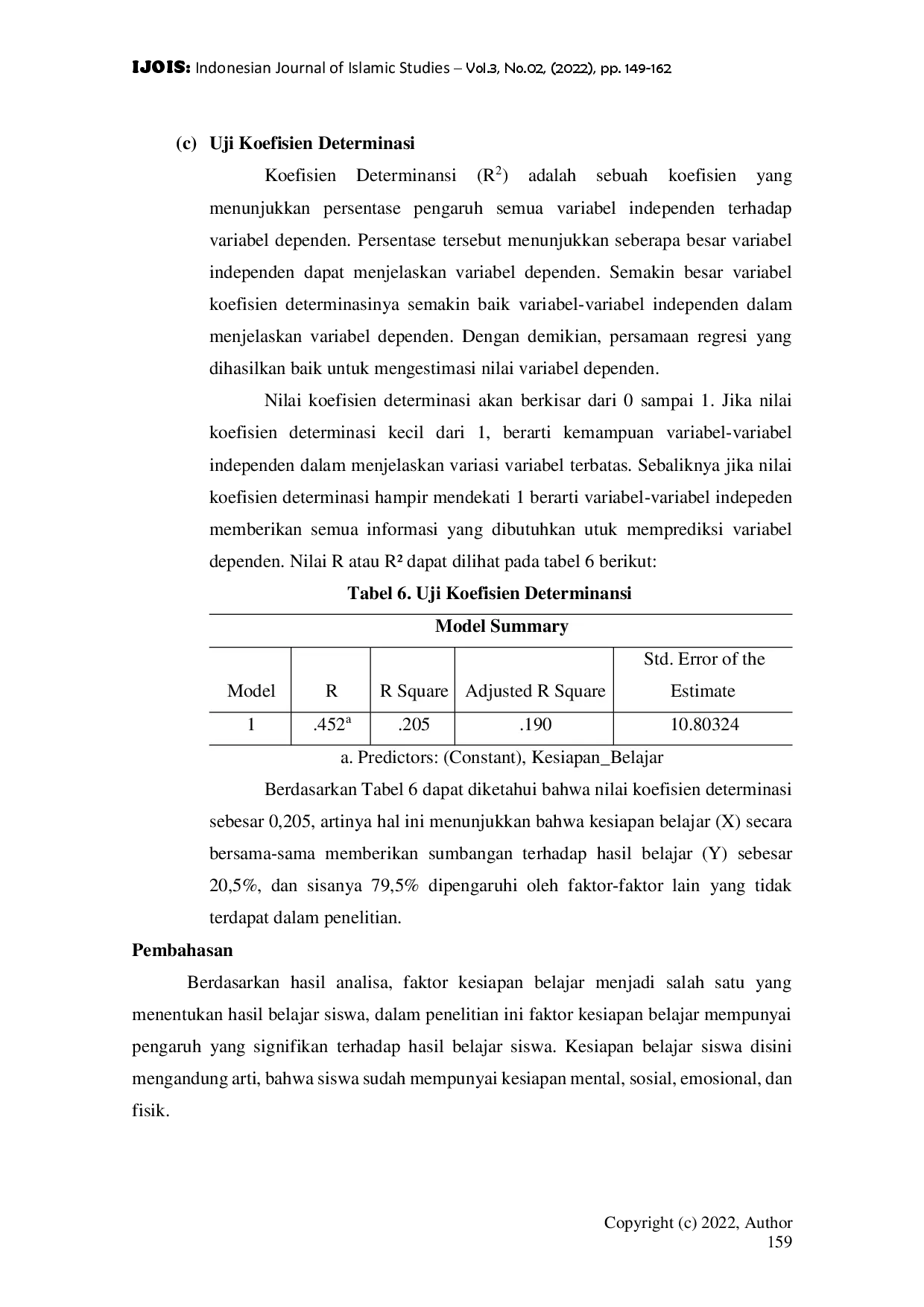
CIVILIZACIVILIZA Abstrak. Kesiapan belajar akan mempengaruhi hasil belajar yang diperoleh siswa. Namun faktanya tidak semua hasil belajar kelas IV SDN 013 Sukamaju KecamatanAbstrak. Kesiapan belajar akan mempengaruhi hasil belajar yang diperoleh siswa. Namun faktanya tidak semua hasil belajar kelas IV SDN 013 Sukamaju Kecamatan
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD This type of research was experimental designs with one group pretest-posttest design. The study used 2 classes, namely class XA as replication class 1This type of research was experimental designs with one group pretest-posttest design. The study used 2 classes, namely class XA as replication class 1
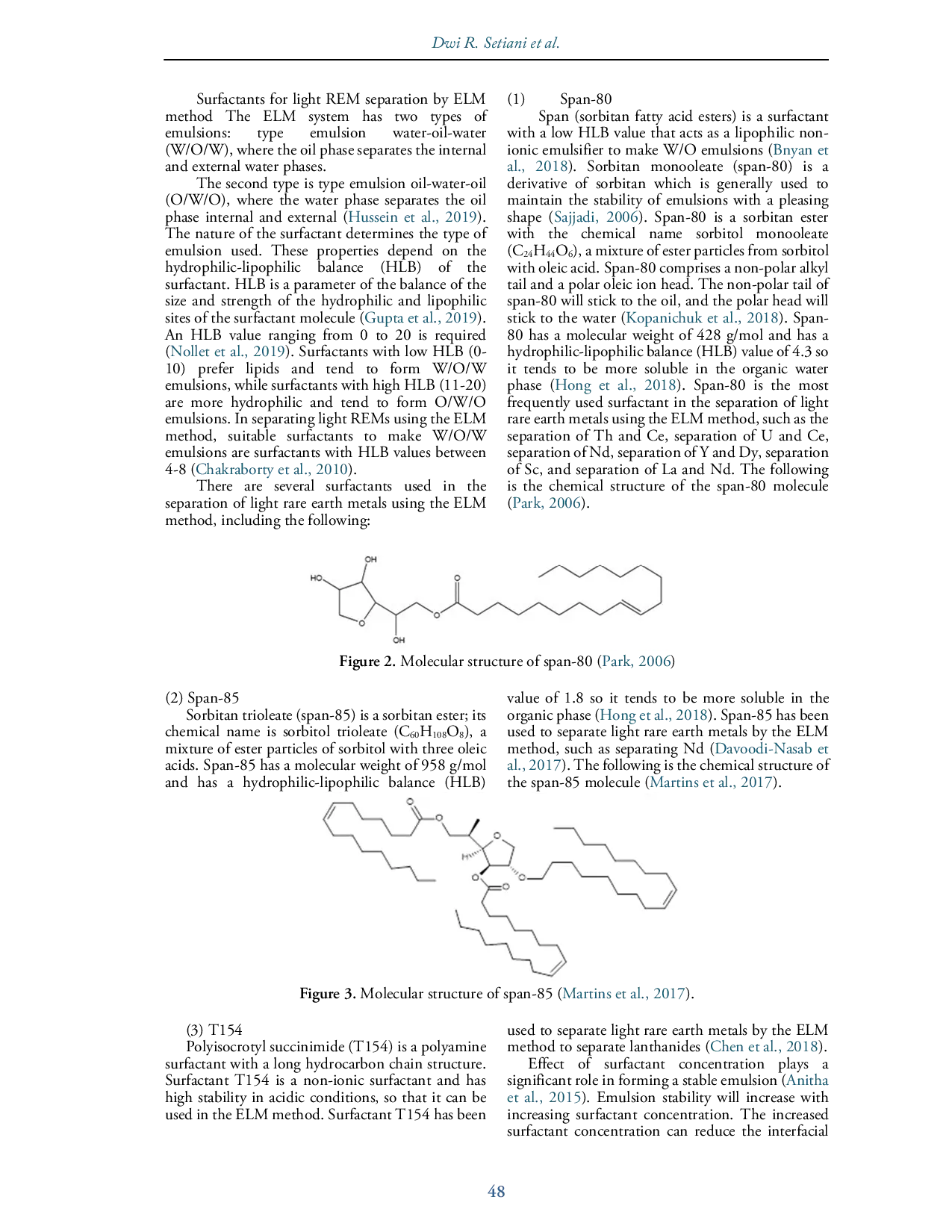
JURNALFKIPUNTADJURNALFKIPUNTAD Surfaktan berperan penting dalam stabilitas emulsi pada proses pemisahan logam tanah jarang ringan menggunakan metode Emulsion Liquid Membrane (ELM). KonsentrasiSurfaktan berperan penting dalam stabilitas emulsi pada proses pemisahan logam tanah jarang ringan menggunakan metode Emulsion Liquid Membrane (ELM). Konsentrasi