KIPMIKIPMI
Communications in Science and TechnologyCommunications in Science and TechnologyAccess to clean water remains a global challenge, which is made worse by the contamination of chemical dyes. The recent innovations of wastewater treatment have been introduced, such as combined biochar with TiO2 photocatalyst. This study proposed to degrade mainly organic pollutants from dyed wastewater using adsorption-photocatalytic of biochar-supported photocatalyst TiO2 (BSP). Mangroves were converted into biochar via hydrothermal carbonization process and combined with TiO2 by a sol-gel method. The composite was then characterized by SEM-EDX, FTIR, and XRD. The degradation performance of the BSPs was optimized with the addition of Titanium (IV) Isopropoxide (TTIP) solution in biochar for 15-25 mL, solution photocatalyst dosage 0.5–1 g/L, initial dyed water concentration at 10 ppm, pH 5.2, and UV-irradiation time from 30 to 240 min in a photocatalytic reactor. The phenomenon of organic pollutants removal was observed based upon the mechanism and dominance of the process and the degradation reaction rate of organic pollutants in dyed wastewater. Methylene blue used as a model dye was degraded 100% through the adsorption-photocatalysis process using BSP. The highest effective degradation performance was found in BSP 20 that had a functional group area of 4.39923 m²/g, a catalyst loading of 0.5 g/L, and the highest degradation rate at k = 0.021 min⁻¹. In subsequent development, the synergistic interaction between biochar and TiO2 presents a promising avenue for the development of advanced wastewater treatment systems targeting the removal of organic pollutants, particularly in textile industry.
The BSP composites demonstrated strong potential for the removal of methylene blue (MB), achieving over 99% efficiency due to the synergistic interaction between biochar and TiO2.The incorporation of TiO2 improved the photodecomposition capability of the composite under UV light, despite reducing its surface functional groups.The study highlights the importance of catalyst dosage in optimizing degradation efficiency and suggests that the BSP composite is a promising candidate for treating dye-contaminated wastewater.
Penelitian lebih lanjut perlu dilakukan untuk mengoptimalkan efisiensi degradasi polutan organik dalam air limbah dengan mempertimbangkan berbagai parameter lingkungan seperti pH, intensitas cahaya, dan durasi iradiasi. Pengembangan material BSP dengan variasi sumber biomassa mangrove yang berbeda, seperti daun atau akar, dapat dieksplorasi untuk meningkatkan kinerja adsorpsi dan fotokatalitik. Selain itu, studi mengenai aplikasi BSP dalam skala pilot atau industri, dengan mempertimbangkan faktor ekonomi dan keberlanjutan, perlu dilakukan untuk menguji kelayakan implementasi teknologi ini dalam mengatasi masalah pencemaran air limbah tekstil secara efektif dan efisien. Penelitian ini diharapkan dapat memberikan kontribusi signifikan dalam pengembangan sistem pengolahan air limbah yang lebih ramah lingkungan dan berkelanjutan.
| File size | 1.51 MB |
| Pages | 9 |
| Short Link | https://juris.id/p-3rs |
| Lookup Links | Google ScholarGoogle Scholar, Semantic ScholarSemantic Scholar, CORE.ac.ukCORE.ac.uk, WorldcatWorldcat, ZenodoZenodo, Research GateResearch Gate, Academia.eduAcademia.edu, OpenAlexOpenAlex, Hollis HarvardHollis Harvard |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
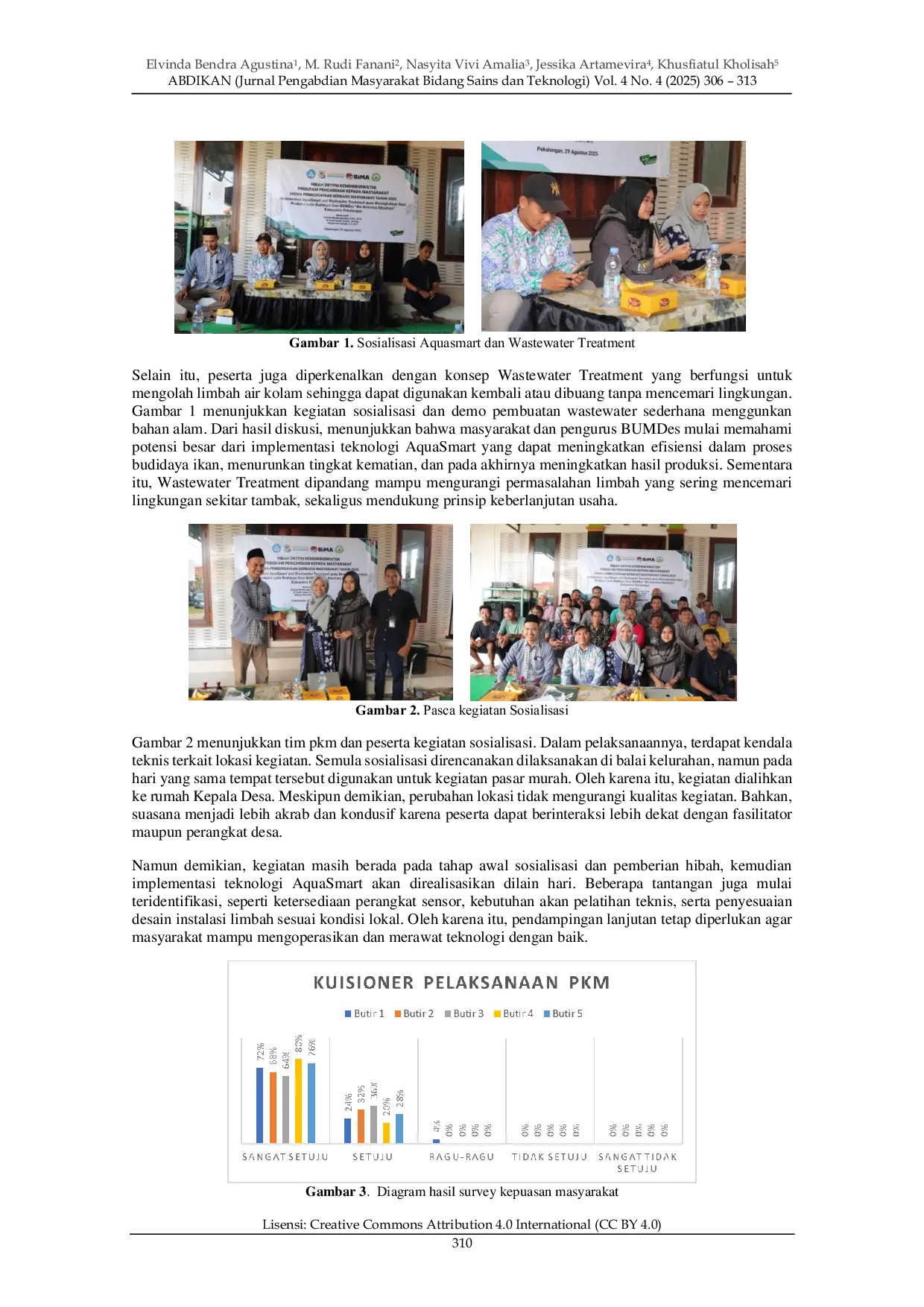
LITERASISAINSLITERASISAINS Kegiatan PkM berdasar pada permasalahan masyarakat desa Api-Api dalam pengelolaan tambak ikan dan udang. Permasalahan tersebut diantaranya tingginya biayaKegiatan PkM berdasar pada permasalahan masyarakat desa Api-Api dalam pengelolaan tambak ikan dan udang. Permasalahan tersebut diantaranya tingginya biaya
KJPUPIKJPUPI Bioreaktor membran (MBR) akhir-akhir ini telah secara luas diterima sebagai teknologi maju untuk pengolahan air limbah domestik dan industri. Tujuan ulasanBioreaktor membran (MBR) akhir-akhir ini telah secara luas diterima sebagai teknologi maju untuk pengolahan air limbah domestik dan industri. Tujuan ulasan
UPIUPI Hasil menunjukkan rata-rata konsentrasi COD, amonium, TN, dan turbidity effluent sebesar 82 ± 6 mg/L, 0,03 ± 0,01 mg/L, 0,75 ± 0,03 mg/L,Hasil menunjukkan rata-rata konsentrasi COD, amonium, TN, dan turbidity effluent sebesar 82 ± 6 mg/L, 0,03 ± 0,01 mg/L, 0,75 ± 0,03 mg/L,
IPBIPB Hal ini dapat digunakan sebagai alat untuk meningkatkan pengelolaan sistem hutan perkotaan dan memantau dampak kebijakan penghijauan perkotaan terhadapHal ini dapat digunakan sebagai alat untuk meningkatkan pengelolaan sistem hutan perkotaan dan memantau dampak kebijakan penghijauan perkotaan terhadap
SAINTEKMUSAINTEKMU Hasilnya menunjukkan adsorpsi optimum pada pH 5 dengan kapasitas maksimum 85,4 mg g⁻¹ untuk Pb(II), 72,1 mg g⁻¹ untuk Cu(II), dan 58,3 mg g⁻¹Hasilnya menunjukkan adsorpsi optimum pada pH 5 dengan kapasitas maksimum 85,4 mg g⁻¹ untuk Pb(II), 72,1 mg g⁻¹ untuk Cu(II), dan 58,3 mg g⁻¹
IPBIPB Pendekatan yang digunakan adalah evaluasi kesesuaian lahan yang mengintegrasikan multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) dan sistem informasi geografis (SIG).Pendekatan yang digunakan adalah evaluasi kesesuaian lahan yang mengintegrasikan multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) dan sistem informasi geografis (SIG).
IPBIPB Temuan ini mengindikasikan perlunya kebijakan yang tidak hanya menyediakan infrastruktur pengelolaan sampah berbasis masyarakat, tetapi juga memperkuatTemuan ini mengindikasikan perlunya kebijakan yang tidak hanya menyediakan infrastruktur pengelolaan sampah berbasis masyarakat, tetapi juga memperkuat
UEUUEU Kondisi ritel saat ini di Indonesia menghadapi banyak masalah, salah satunya adalah distorsi pendapatan baru, yaitu ritel yang tidak memiliki tempat atauKondisi ritel saat ini di Indonesia menghadapi banyak masalah, salah satunya adalah distorsi pendapatan baru, yaitu ritel yang tidak memiliki tempat atau
Useful /
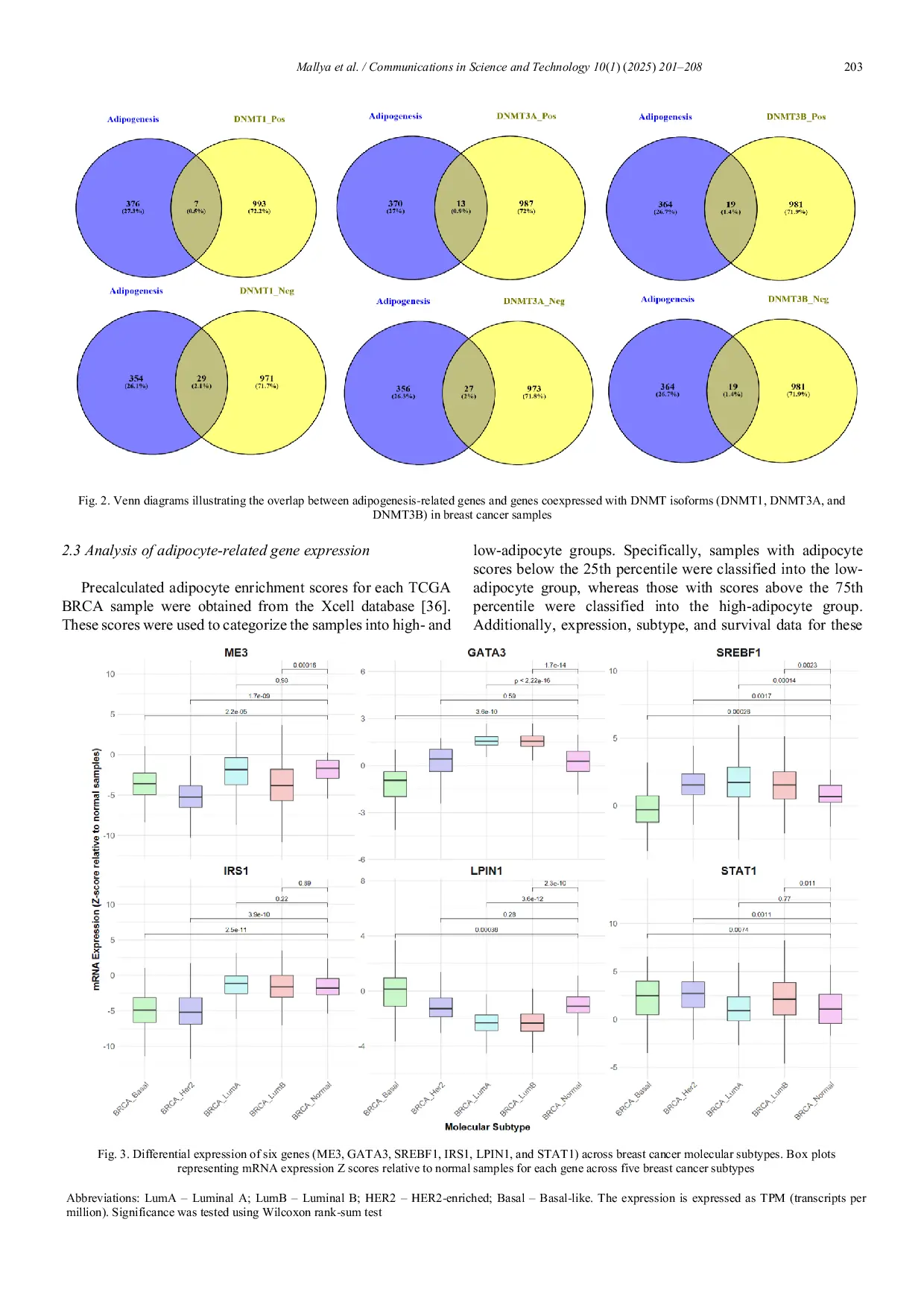
KIPMIKIPMI Studi ini menyajikan analisis komprehensif mengenai metilasi DNA yang dimediasi DNMT, adipogenesis, dan patogenesis kanker payudara, mengidentifikasi genStudi ini menyajikan analisis komprehensif mengenai metilasi DNA yang dimediasi DNMT, adipogenesis, dan patogenesis kanker payudara, mengidentifikasi gen
IPBIPB Studi ini menunjukkan bahwa teknologi e-learning mampu meningkatkan kualitas proses belajar-mengajar di institusi pendidikan. Hasil penelitian menunjukkanStudi ini menunjukkan bahwa teknologi e-learning mampu meningkatkan kualitas proses belajar-mengajar di institusi pendidikan. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan
IPBIPB Penerapan model ini memberikan kontribusi positif terhadap proses pembelajaran yang lebih aktif dan kritis. Disarankan kepada guru untuk menerapkan modelPenerapan model ini memberikan kontribusi positif terhadap proses pembelajaran yang lebih aktif dan kritis. Disarankan kepada guru untuk menerapkan model
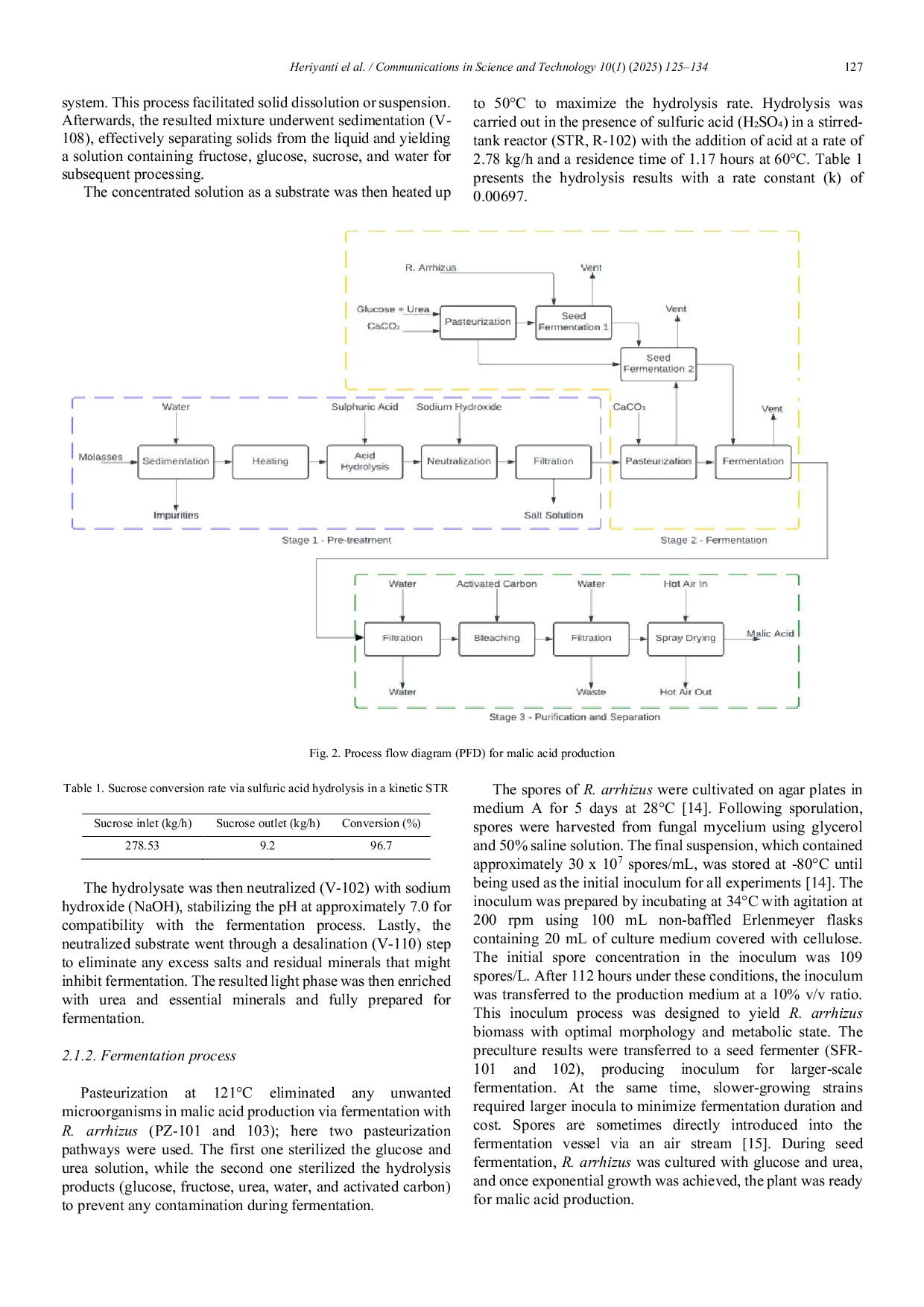
KIPMIKIPMI Sensitivity analysis highlighted the selling price of malic acid as the most important economic factor. This feasibility study provides a novel approachSensitivity analysis highlighted the selling price of malic acid as the most important economic factor. This feasibility study provides a novel approach