UNIVMEDUNIVMED
Universa MedicinaUniversa MedicinaGonorrhea is the second most common sexually transmitted bacterial infection (STI), following Chlamydia. Neisseria gonorrhoeae resistant to antibiotics are increasing globally. In recent years, many studies have reported reduced susceptibility of N.gonorrhoeae to almost all clinically useful antibiotics and also reported cases of multi-resistance. Resistance mechanisms for N. gonorrhoeae can occur through genetic and non-genetic changes. Resistance to cefixime and azithromycin as first-line antibiotics for monotherapy recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) has been reported from several countries. Genetic changes were reported as the main cause of N.gonorrhoeae resistance to cefixime and azithromycin. Based on the WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, countries are increasingly using a combination of cephalosporin and azithromycin for the treatment of gonorrhea. The aim of this review is to analyze genetic variation of N.gonorrhoeae resistance to cefixime and azithromycin. Articles published in English in the last 12 years (from 2010 to 2021) were retrieved from Science Direct, PubMed, Springerlink, Oxford and Nature using relevant searching terms. Mutants of cefixime-resistant N.gonorrhoeae are mediated by mosaic and non-mosaic penA genes encoding penicillin binding protein 2. In addition, mutations in the repressor and promoter genes of mtrR were also found that caused overexpression of the microbial efflux pump. Meanwhile, N. gonorrhoeae resistance to azithromycin reportedly occurs through two strategies, namely overexpression of the efflux pump (mutation of the mtrR codon region) and decreased affinity for antibiotics (single base mutation in the 23S rRNA gene). With the limited choice of antibiotics for the management of N.gonorrhoeae, it is necessary to do regular surveillance for monitoring drug resistance. By understanding the mechanism of resistance, the use of these antibiotics can be rationally optimized.
Modifikasi protein target merupakan mekanisme utama resistensi N.gonorrhoeae terhadap azithromycin lebih dipengaruhi oleh overexpression pompa efflux.WHO merekomendasikan pemberian cefixime dan azithromycin untuk pengobatan gonore guna mengurangi angka resistensi.Pemahaman terhadap mekanisme resistensi ini penting untuk optimasi penggunaan antibiotik.
Berdasarkan pemahaman mekanisme resistensi antibiotik pada *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*, penelitian lanjutan perlu difokuskan pada pengembangan strategi terapi baru yang dapat mengatasi resistensi ini. Salah satu ide penelitian adalah menguji efektivitas kombinasi antibiotik baru yang menargetkan jalur resistensi yang berbeda, misalnya kombinasi yang menghambat pompa efflux sekaligus mengganggu sintesis protein bakteri. Selain itu, penelitian lebih lanjut diperlukan untuk mengidentifikasi dan memvalidasi target obat baru pada *N. gonorrhoeae* yang belum terpengaruh oleh mekanisme resistensi yang ada, seperti protein yang berperan penting dalam pembentukan biofilm atau virulensi bakteri. Terakhir, studi epidemiologi yang komprehensif perlu dilakukan untuk memantau penyebaran gen resistensi dan mengidentifikasi faktor-faktor risiko yang berkontribusi terhadap peningkatan resistensi antibiotik pada *N. gonorrhoeae* di berbagai populasi, sehingga dapat dirumuskan strategi pencegahan dan pengendalian infeksi yang lebih efektif.
- Decreased susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Switzerland to Cefixime and Ceftriaxone:... doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-603Decreased susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Switzerland to Cefixime and Ceftriaxone doi 10 1186 1471 2334 13 603
- 0. loading academic.oup.com/jac/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/jac/dku0260 loading academic oup jac article lookup doi 10 1093 jac dku026
- Genetic Characterization and Enhanced Surveillance of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae Strain,... doi.org/10.3201/eid2509.190407Genetic Characterization and Enhanced Surveillance of Ceftriaxone Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae Strain doi 10 3201 eid2509 190407
- Emergence of ceftriaxone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains harbouring a novel mosaic penA gene... doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkz530Emergence of ceftriaxone resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains harbouring a novel mosaic penA gene doi 10 1093 jac dkz530
| File size | 2.08 MB |
| Pages | 11 |
| DMCA | ReportReport |
Related /
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Kesimpulan Anestesi spinal dengan sufentanil tidak meningkatkan durasi tahap persalinan. Disarankan agar penelitian selanjutnya dilakukan dengan ukuranKesimpulan Anestesi spinal dengan sufentanil tidak meningkatkan durasi tahap persalinan. Disarankan agar penelitian selanjutnya dilakukan dengan ukuran
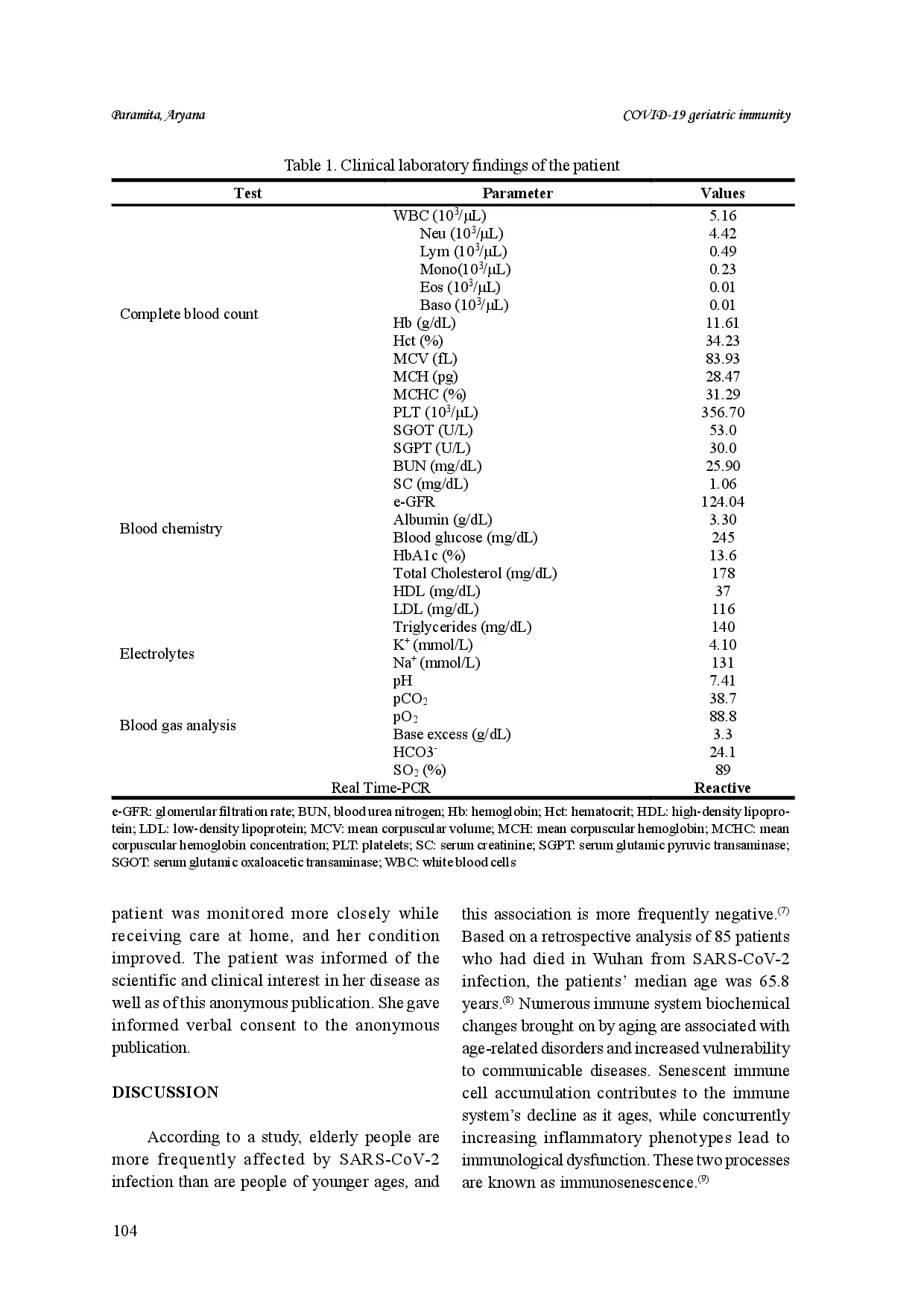
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Penyebab utama kematian dan tingginya tingkat keparahan morbilitas pada populasi lansia akibat infeksi COVID-19 dikarenakan berbagai faktor, termasuk penurunanPenyebab utama kematian dan tingginya tingkat keparahan morbilitas pada populasi lansia akibat infeksi COVID-19 dikarenakan berbagai faktor, termasuk penurunan
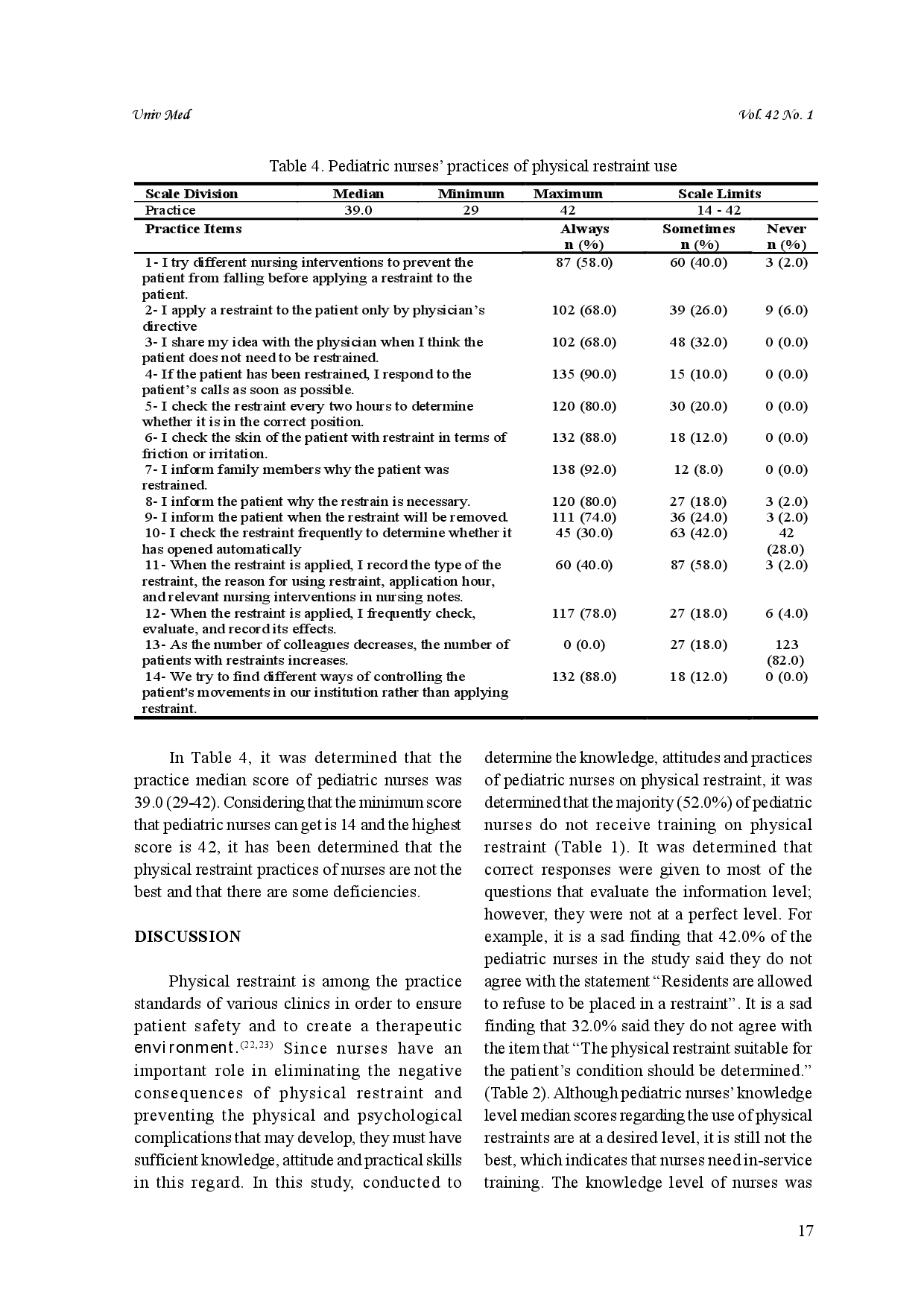
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Kesimpulan: Tingkat pengetahuan perawat pediatrik tentang penahanan fisik cukup baik dan sikap mereka positif, namun terdapat kekurangan dalam praktik.Kesimpulan: Tingkat pengetahuan perawat pediatrik tentang penahanan fisik cukup baik dan sikap mereka positif, namun terdapat kekurangan dalam praktik.
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Metode penelitian menggunakan pendekatan cross-sectional pada 462 wanita muda. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 73,8% wanita merupakan pemakan emosional.Metode penelitian menggunakan pendekatan cross-sectional pada 462 wanita muda. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 73,8% wanita merupakan pemakan emosional.
Useful /
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Tujuan studi ini adalah untuk membandingkan efek olahraga aerobik dan olahraga kekuatan terhadap komposisi tubuh dan kualitas hidup (QoL) wanita berlebihanTujuan studi ini adalah untuk membandingkan efek olahraga aerobik dan olahraga kekuatan terhadap komposisi tubuh dan kualitas hidup (QoL) wanita berlebihan
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Frekuensi sakit kepala terkait penggunaan PPE tinggi pada petugas kesehatan COVID-19. Level PPE merupakan faktor risiko terjadinya sakit kepala. StrategiFrekuensi sakit kepala terkait penggunaan PPE tinggi pada petugas kesehatan COVID-19. Level PPE merupakan faktor risiko terjadinya sakit kepala. Strategi
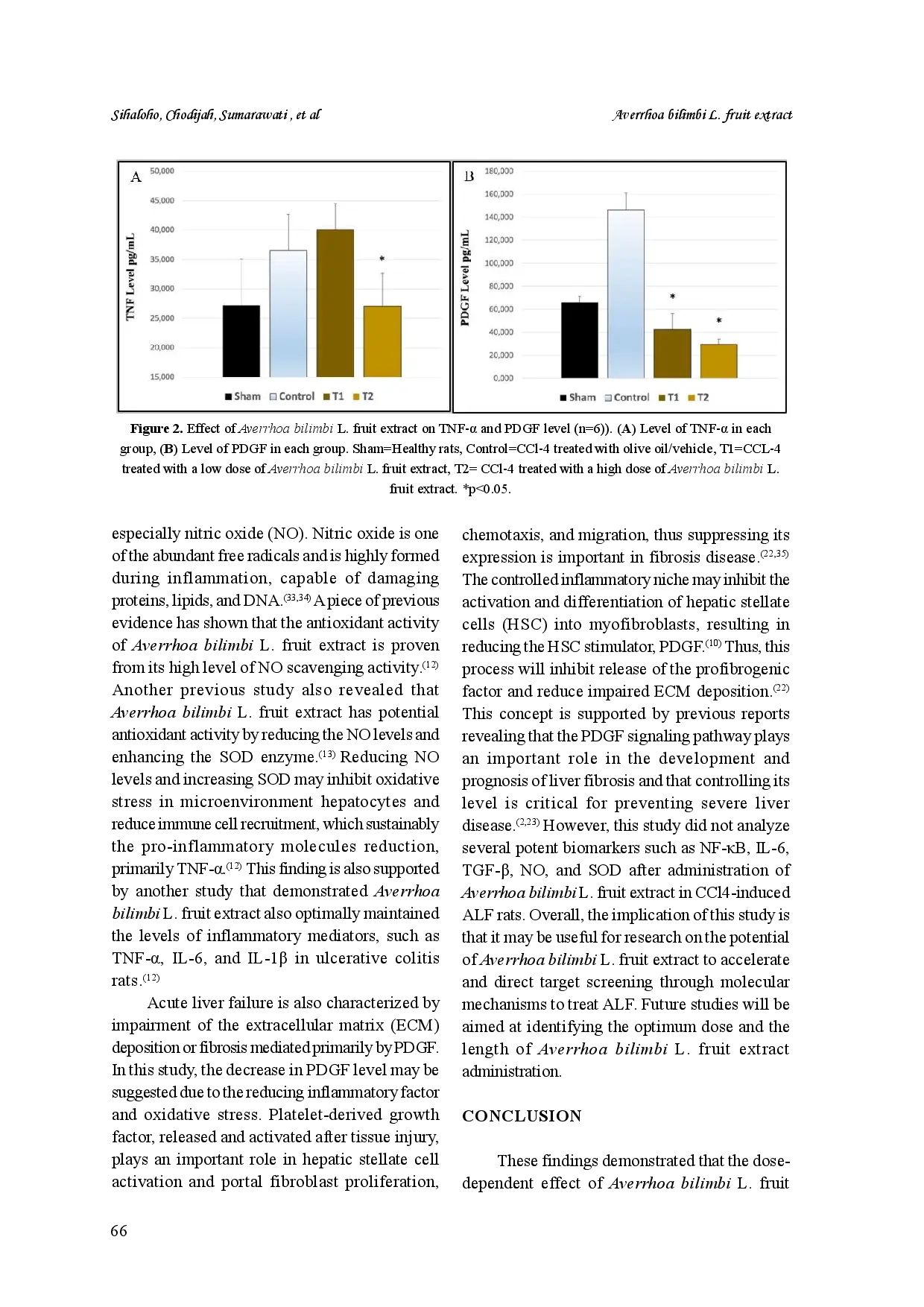
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Kelompok T1 diberikan CCl4 dan ekstrak buah A. bilimbi dosis 500 mg/kgBB, sedangkan kelompok T2 diberikan CCl4 dan ekstrak buah A. bilimbi dosis 750 mg/kgBB.Kelompok T1 diberikan CCl4 dan ekstrak buah A. bilimbi dosis 500 mg/kgBB, sedangkan kelompok T2 diberikan CCl4 dan ekstrak buah A. bilimbi dosis 750 mg/kgBB.
UNIVMEDUNIVMED Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menilai biofilm sejenis dan dual- spesies Escherichia coli (kode A), Staphylococcus aureus (kode B), Klebsiella pneumoniaePenelitian ini bertujuan untuk menilai biofilm sejenis dan dual- spesies Escherichia coli (kode A), Staphylococcus aureus (kode B), Klebsiella pneumoniae