IARNIARN
Indonesia Accounting Research JournalIndonesia Accounting Research JournalThis study aims to examine the integration of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and the Theory of Constraints (TOC) as a conceptual framework for developing environmentally conscious and efficient environmental cost management. A systematic literature review was conducted on twenty relevant scientific publications to identify key patterns, findings, and integration opportunities between the two approaches. The results indicate that ABC enhances the accuracy of environmental cost information by tracing activity-based sources of energy waste, emissions, and waste generation, while TOC focuses on identifying and managing systemic constraints that limit efficiency and sustainability in production processes. The integration of ABC and TOC provides a comprehensive environmental cost management framework that goes beyond economic efficiency and strengthens organizational awareness of ecological limits. Conceptually, this synergy contributes to the advancement of environmental accounting as a knowledge-based system that links economic value with ecological responsibility and offers future development potential through digital technologies such as big data analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence–based environmental management.
The study concludes that the synergy between Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and the Theory of Constraints (TOC) provides a comprehensive framework for environmental cost management that extends beyond conventional cost reduction strategies.ABC enables organizations to identify hidden environmental costs—such as energy use, emissions, and waste—through activity-based causal analysis, while TOC focuses on identifying systemic constraints that limit operational efficiency and environmental sustainability.The integration of these approaches creates a balance between analytical precision and strategic focus, allowing organizations to prioritize improvement efforts in areas where economic efficiency aligns with ecological responsibility.Strategically, this framework enables organizations to align economic performance with environmental carrying capacity by focusing improvement efforts on critical activities and constraints that simultaneously affect cost efficiency and ecological impact, thereby supporting proactive, responsible, and long-term sustainable value creation.
Berdasarkan latar belakang, metode, hasil, keterbatasan, dan saran penelitian lanjutan yang ada dalam paper, berikut adalah saran penelitian lanjutan yang baru: Pertama, penelitian selanjutnya dapat menginvestigasi bagaimana penerapan model ABC-TOC dapat diintegrasikan dengan sistem digital seperti IoT dan big data analytics untuk meningkatkan akurasi dan real-time monitoring biaya lingkungan. Kedua, penelitian dapat mengeksplorasi bagaimana faktor-faktor perilaku dan budaya organisasi mempengaruhi efektivitas implementasi model ABC-TOC dalam mendorong praktik keberlanjutan. Ketiga, penelitian dapat menguji efektivitas model ABC-TOC dalam konteks industri yang berbeda, seperti sektor jasa atau pariwisata, untuk mengidentifikasi tantangan dan peluang spesifik dalam pengelolaan biaya lingkungan. Integrasi ketiga saran ini akan memberikan pemahaman yang lebih komprehensif tentang bagaimana organisasi dapat memanfaatkan model ABC-TOC untuk mencapai efisiensi ekonomi dan keberlanjutan lingkungan secara bersamaan, serta mengidentifikasi faktor-faktor kunci yang mempengaruhi keberhasilan implementasi model tersebut. Dengan demikian, penelitian ini dapat memberikan kontribusi signifikan bagi pengembangan praktik akuntansi lingkungan yang lebih efektif dan relevan dalam mendukung pengambilan keputusan strategis yang bertanggung jawab secara sosial dan lingkungan.
| File size | 391.22 KB |
| Pages | 10 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
STIKES BHMSTIKES BHM Pelayanan farmasi di rumah sakit dapat dikatakan efisien jika pengelolaan obat, termasuk antibiotik, dilakukan sesuai peraturan dan di bawah pengawasanPelayanan farmasi di rumah sakit dapat dikatakan efisien jika pengelolaan obat, termasuk antibiotik, dilakukan sesuai peraturan dan di bawah pengawasan
GLOBALHEALTHSCIENCEGROUPGLOBALHEALTHSCIENCEGROUP Wawancara menunjukkan bahwa 90% peserta merasa lebih percaya diri dan siap menyusui secara eksklusif. Konseling dan pendampingan secara langsung terbuktiWawancara menunjukkan bahwa 90% peserta merasa lebih percaya diri dan siap menyusui secara eksklusif. Konseling dan pendampingan secara langsung terbukti
ITSKHATULISTIWAITSKHATULISTIWA Variabel E-Commerce dan pelatihan kewirausahaan mempengaruhi variabel untuk meningkatkan volume penjualan sebesar 29. 5% sisanya dijelaskan oleh variabelVariabel E-Commerce dan pelatihan kewirausahaan mempengaruhi variabel untuk meningkatkan volume penjualan sebesar 29. 5% sisanya dijelaskan oleh variabel
POLSRIPOLSRI Data didapatkan dengan wawancara dan observasi ke UMKM. Perhitungan pendekatan ABC menunjukkan hasil yang sesungguhnya sebab mengalokasikan setiap komponenData didapatkan dengan wawancara dan observasi ke UMKM. Perhitungan pendekatan ABC menunjukkan hasil yang sesungguhnya sebab mengalokasikan setiap komponen
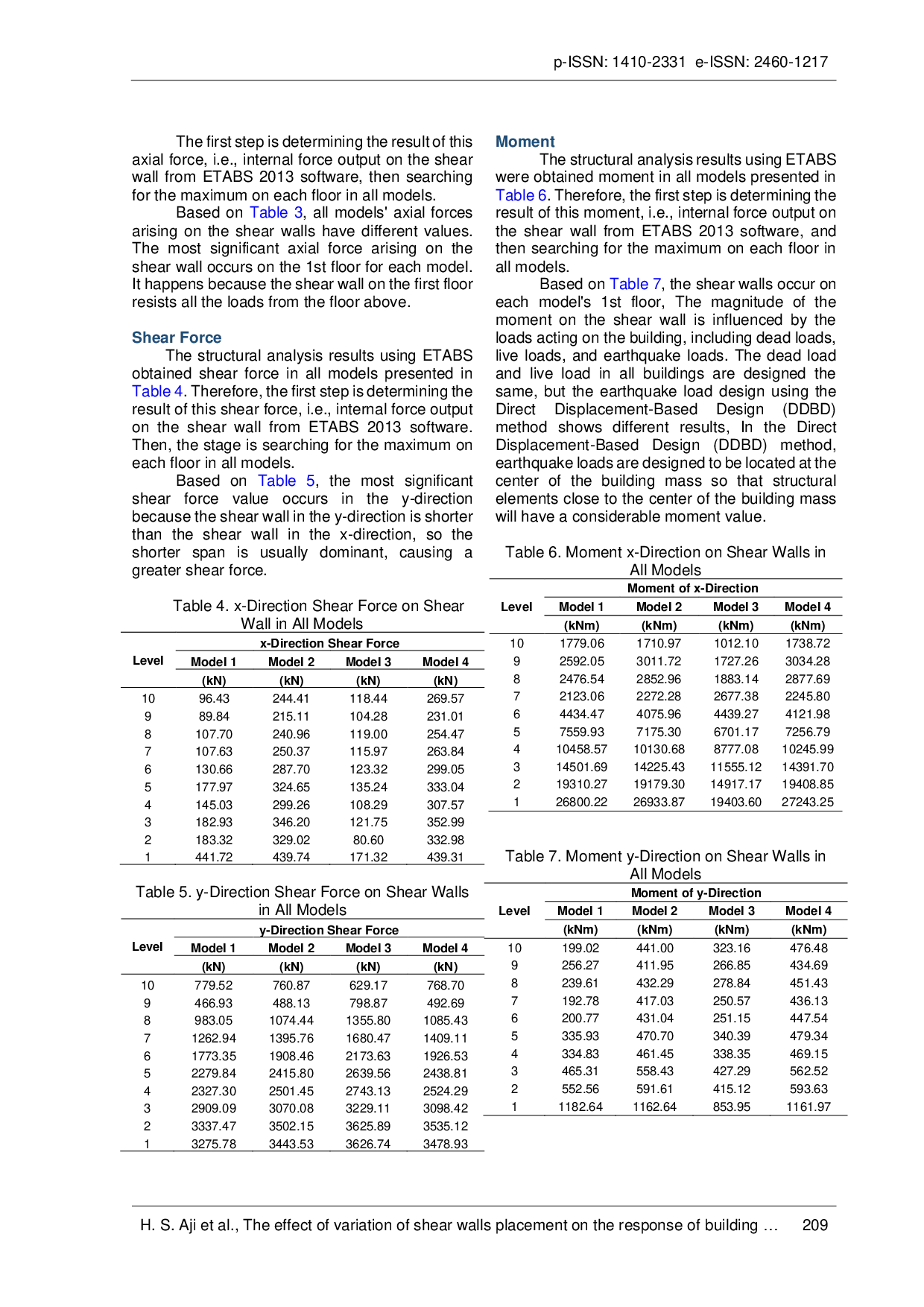
UMBUMB Oleh karena itu, disarankan untuk penelitian lanjutan menempatkan dinding geser sesuai kondisi bangunan yang teratur atau tidak teratur, kelas lokasi tanahOleh karena itu, disarankan untuk penelitian lanjutan menempatkan dinding geser sesuai kondisi bangunan yang teratur atau tidak teratur, kelas lokasi tanah
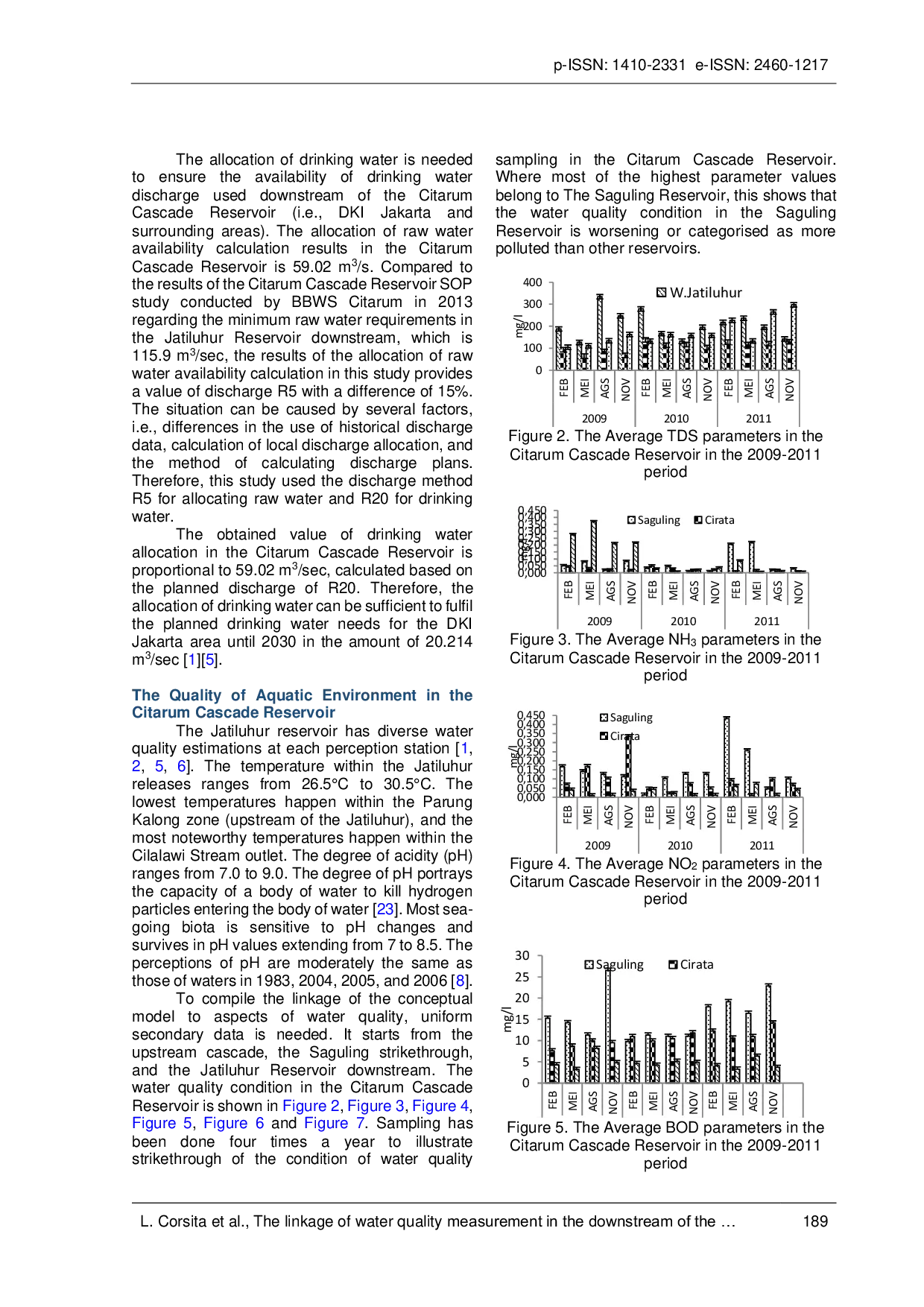
UMBUMB The waters of the Citarum Cascade Reservoir have been polluted by organic matter that is easily biodegradable and unfit for use as a source of raw drinkingThe waters of the Citarum Cascade Reservoir have been polluted by organic matter that is easily biodegradable and unfit for use as a source of raw drinking
UMBUMB Demikian pula, amplitudo yaw keseluruhan di sisi kanan atau kiri meningkat signifikan, dipengaruhi oleh panjang tali tarik dari 1,5L hingga 2L. PerbedaanDemikian pula, amplitudo yaw keseluruhan di sisi kanan atau kiri meningkat signifikan, dipengaruhi oleh panjang tali tarik dari 1,5L hingga 2L. Perbedaan
UMBUMB Temuan ini mungkin juga disebabkan oleh variasi ketinggian lantai yang dipertimbangkan, R = 3 hingga 8, dan kapasitas rotasi, yang juga berkontribusi terhadapTemuan ini mungkin juga disebabkan oleh variasi ketinggian lantai yang dipertimbangkan, R = 3 hingga 8, dan kapasitas rotasi, yang juga berkontribusi terhadap
Useful /
STIKES BHMSTIKES BHM Hasil molecular docking menunjukkan bahwa Naringin (glikosida) menghasilkan skor afinitas ikatan terbaik. Namun naringenin (aglikon) menunjukkan skor afinitasHasil molecular docking menunjukkan bahwa Naringin (glikosida) menghasilkan skor afinitas ikatan terbaik. Namun naringenin (aglikon) menunjukkan skor afinitas
KETERAPIAN FISIKKETERAPIAN FISIK Metode: Penelitian ini merupakan tinjauan sistematis dan meta-analisis dari sembilan studi kohort yang melibatkan populasi yang beragam untuk mengevaluasiMetode: Penelitian ini merupakan tinjauan sistematis dan meta-analisis dari sembilan studi kohort yang melibatkan populasi yang beragam untuk mengevaluasi
LODDOSINSTITUTELODDOSINSTITUTE Implementasi program berbasis CNF juga memberikan gambaran praktis mengenai bagaimana teori automata dapat diterapkan dalam sistem komputasi modern. OlehImplementasi program berbasis CNF juga memberikan gambaran praktis mengenai bagaimana teori automata dapat diterapkan dalam sistem komputasi modern. Oleh
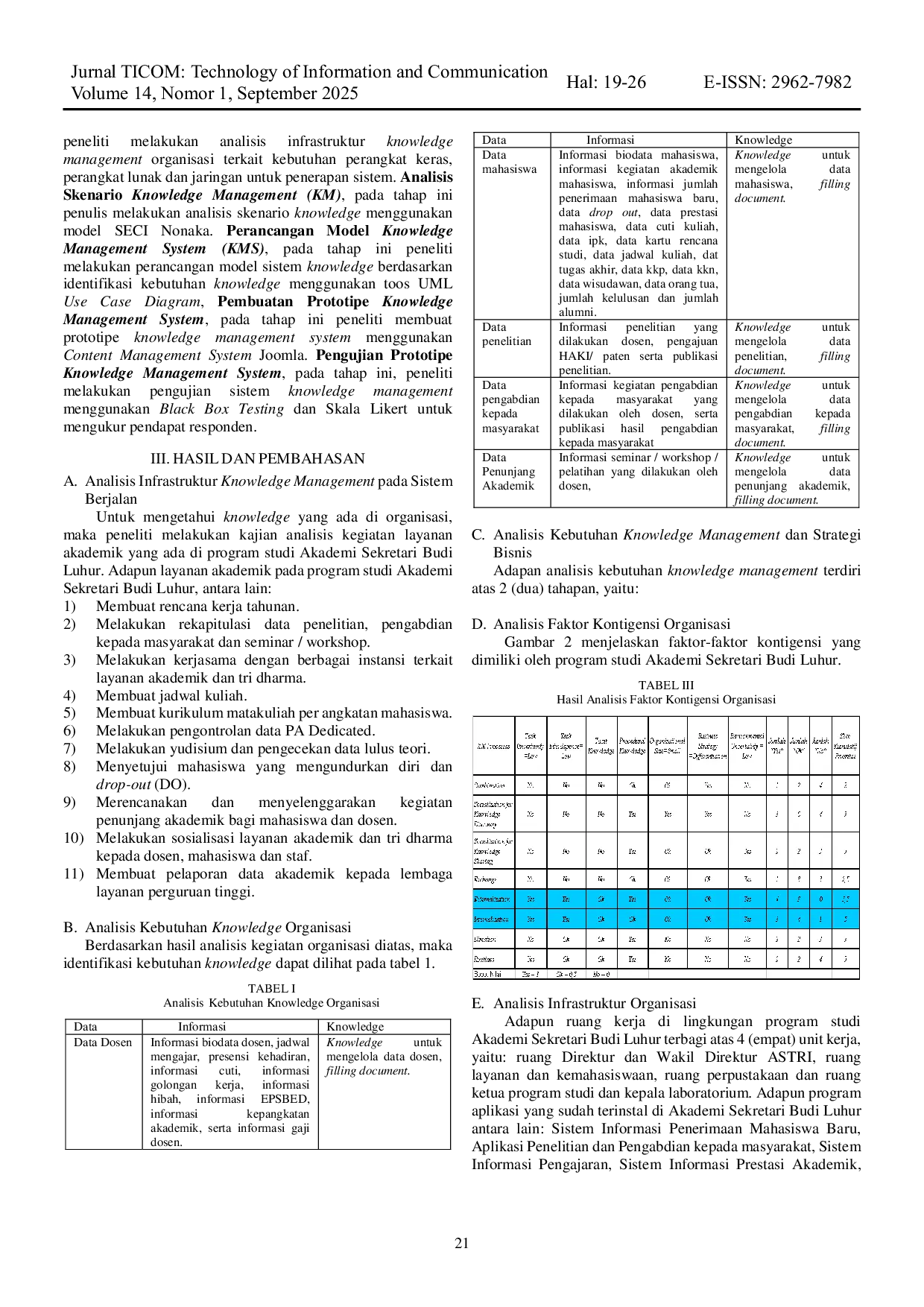
APTIKOMAPTIKOM Fitur utama yang mendukung Knowledge Management (Socialization, Externalization, Combination, dan Internalization) meliputi percakapan elektronik, diskusiFitur utama yang mendukung Knowledge Management (Socialization, Externalization, Combination, dan Internalization) meliputi percakapan elektronik, diskusi