BALAIPUBLIKASIBALAIPUBLIKASI
AMPLITUDO : Journal of Science and Technology InnovationAMPLITUDO : Journal of Science and Technology InnovationFood waste (FW) and coconut waste (CW) contribute significantly to environmental pollution, highlighting the need for sustainable waste management solutions. This study investigates the anaerobic digestion (AD) of FW and dried CW, comparing the efficiency of single and mixing digestion approaches in biogas production. The research examines the physical properties of both substrates and evaluates their biogas production potential using anaerobic single and mixing digestion techniques. Standard methods were employed to analyse total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), and pH. The experiments were conducted in Duran bottles at mesophilic temperatures (26°C–32°C) with a set inoculum-to-sample ratio. Biogas production was measured using the water displacement method over 10 days. The TS values for FW and CW were 46.00% (±0.05) and 60.00% (±0.04), respectively, while their VS values were 97.73% (±0.05) and 93.75% (±0.07), respectively. The pH analysis indicated that both substrates were in an acidic state; the value was near the optimum value of AD. Biogas recovery results indicates that mixing digestion of FW and CW produced the highest yield, reaching 786.00 mL (±0.02) on day 8. In contrast, single digestion of FW and CW yielded 425.0 mL (±0.04) (day 8) and 475.0 mL (±0.05) (day 7), respectively. These findings demonstrate that mixing digestion significantly enhances biogas production due to improved nutrient balance and microbial activity. Additionally, mixing digestion stabilizes the AD process, leading to greater efficiency and energy recovery. This study highlights the potential of FW and CW as viable feedstocks for biogas generation, offering a sustainable waste management alternative. By optimizing AD systems, this research contributes to renewable energy development and supports sustainable waste utilization practices.
The study concluded that mixing digestion of food waste (FW) and coconut waste (CW) yielded the highest biogas production compared to single digestion of either substrate.This enhancement is attributed to improved nutrient balance and increased microbial activity within the mixed digestion process.Furthermore, the research highlights the potential of utilizing FW and CW as sustainable feedstocks for biogas generation, contributing to renewable energy development and waste management solutions.
Berdasarkan hasil penelitian ini, beberapa saran penelitian lanjutan dapat diajukan. Pertama, perlu dilakukan penelitian lebih lanjut untuk mengoptimalkan rasio pencampuran FW dan CW untuk mencapai produksi biogas yang paling efisien, dengan mempertimbangkan variasi komposisi limbah yang berbeda. Kedua, studi tentang pengaruh pretreatment terhadap FW dan CW, seperti hidrolisis termal atau ultrasonikasi, dapat dilakukan untuk meningkatkan biodegradabilitas dan produksi biogas. Ketiga, penelitian mengenai penggunaan berbagai jenis inokulum, termasuk inokulum yang berasal dari lingkungan yang berbeda, dapat dieksplorasi untuk meningkatkan kinerja AD dan stabilitas proses. Penelitian-penelitian ini diharapkan dapat memberikan pemahaman yang lebih mendalam tentang potensi optimalisasi sistem AD untuk pemanfaatan limbah organik secara berkelanjutan dan produksi energi terbarukan yang lebih efisien. Dengan demikian, penelitian lanjutan ini dapat berkontribusi pada pengembangan solusi pengelolaan limbah yang lebih ramah lingkungan dan berkelanjutan.
- 0. iv m9 rb lx ly qry uv pe xk oc 5jb xb zpn 4c5 xg 3hy 6v kk 2p kw tg qp nh jg vr zw d9 mc wt qi io... doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.7035250 iv m9 rb lx ly qry uv pe xk oc 5jb xb zpn 4c5 xg 3hy 6v kk 2p kw tg qp nh jg vr zw d9 mc wt qi io doi 10 3389 fmicb 2021 703525
- Enhancing Biogas Production Via Single and Mixing Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste and Coconut Waste... doi.org/10.56566/amplitudo.v4i2.315Enhancing Biogas Production Via Single and Mixing Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste and Coconut Waste doi 10 56566 amplitudo v4i2 315
| File size | 231.41 KB |
| Pages | 7 |
| DMCA | Report |
Related /
BERUGAKBACABERUGAKBACA Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mencerminkan kehidupan sosial yang seimbang antara dunia dan akhirat. Hal ini penting untuk dilakukan sebagaimana pentingnyaPenelitian ini bertujuan untuk mencerminkan kehidupan sosial yang seimbang antara dunia dan akhirat. Hal ini penting untuk dilakukan sebagaimana pentingnya
BERUGAKBACABERUGAKBACA Selain itu, hasil ini juga berguna sebagai referensi teknis dalam perkuatan struktur bangunan serupa. Berdasarkan hasil perhitungan simpangan total maksimumSelain itu, hasil ini juga berguna sebagai referensi teknis dalam perkuatan struktur bangunan serupa. Berdasarkan hasil perhitungan simpangan total maksimum
BALAIPUBLIKASIBALAIPUBLIKASI Metode penelitian yang digunakan adalah deskriptif dan analitis, dengan data diperoleh dari dokumen yang terindeks oleh Google Scholar dari tahun 2015-2024Metode penelitian yang digunakan adalah deskriptif dan analitis, dengan data diperoleh dari dokumen yang terindeks oleh Google Scholar dari tahun 2015-2024
BALAIPUBLIKASIBALAIPUBLIKASI Dengan meninjau kondisi manajemen limbah masa lalu dan sekarang di Bangladesh, serta membandingkan praktik di negara tetangga seperti India, Bhutan, SriDengan meninjau kondisi manajemen limbah masa lalu dan sekarang di Bangladesh, serta membandingkan praktik di negara tetangga seperti India, Bhutan, Sri
UNCMUNCM Penelitian ini mengkaji integrasi nilai-nilai kearifan lokal dalam pendidikan multikultural di sekolah dasar dan pengaruhnya terhadap sikap multikulturalPenelitian ini mengkaji integrasi nilai-nilai kearifan lokal dalam pendidikan multikultural di sekolah dasar dan pengaruhnya terhadap sikap multikultural
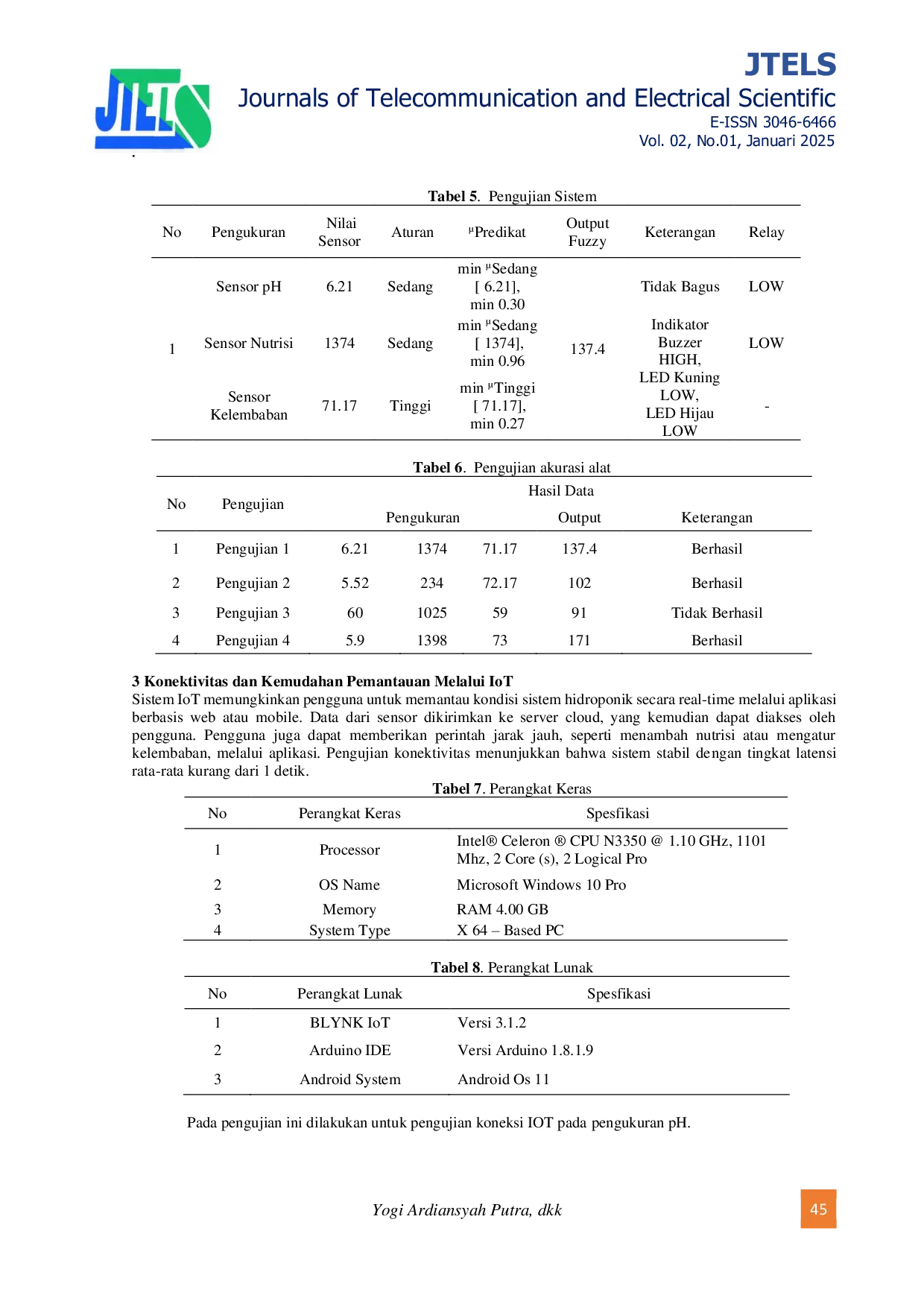
HARAPANHARAPAN (2) Perangkat lunak dirancang menggunakan bahasa C dan Arduino IDE serta berfungsi dengan baik. (3) Modul Wemos mengirimkan koordinat ke aplikasi Blynk(2) Perangkat lunak dirancang menggunakan bahasa C dan Arduino IDE serta berfungsi dengan baik. (3) Modul Wemos mengirimkan koordinat ke aplikasi Blynk
HARAPANHARAPAN Penelitian ini mencakup eksperimen langsung dengan pengukuran daya menggunakan alat ukur terkalibrasi untuk memastikan keakuratan hasil. Pengujian dilakukanPenelitian ini mencakup eksperimen langsung dengan pengukuran daya menggunakan alat ukur terkalibrasi untuk memastikan keakuratan hasil. Pengujian dilakukan
HARAPANHARAPAN Sementara Mesin press 3000 T ini hanya menggunakan 2 motor berskala besar saja. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui penggunaan daya listrikSementara Mesin press 3000 T ini hanya menggunakan 2 motor berskala besar saja. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui penggunaan daya listrik
Useful /
UINSAIZUUINSAIZU Pendekatan kualitatif dalam kerangka fenomenologi digunakan. Data penelitian dikumpulkan melalui observasi partisipatif di pasar tradisional, wawancaraPendekatan kualitatif dalam kerangka fenomenologi digunakan. Data penelitian dikumpulkan melalui observasi partisipatif di pasar tradisional, wawancara
BALAIPUBLIKASIBALAIPUBLIKASI Penelitian ini mengevaluasi dampak intervensi pengobatan (pemberian oksitetrasiklin 20% dan Penistripe) serta kampanye vaksinasi masal terhadap tingkatPenelitian ini mengevaluasi dampak intervensi pengobatan (pemberian oksitetrasiklin 20% dan Penistripe) serta kampanye vaksinasi masal terhadap tingkat
BALAIPUBLIKASIBALAIPUBLIKASI Di wilayah metropolitan Bauchi, rata‑rata volume limbah yang dihasilkan adalah sekitar 0,003 m³/orang/hari untuk daerah berpadat tinggi dan 0,005 m³/orang/hariDi wilayah metropolitan Bauchi, rata‑rata volume limbah yang dihasilkan adalah sekitar 0,003 m³/orang/hari untuk daerah berpadat tinggi dan 0,005 m³/orang/hari
HARAPANHARAPAN Selain itu, rancangan ini menawarkan efisiensi operasional, pengurangan kesalahan manusia, serta kemudahan dalam pengelolaan pertanian hidroponik. HasilSelain itu, rancangan ini menawarkan efisiensi operasional, pengurangan kesalahan manusia, serta kemudahan dalam pengelolaan pertanian hidroponik. Hasil