IRPIIRPI
MALCOM: Indonesian Journal of Machine Learning and Computer ScienceMALCOM: Indonesian Journal of Machine Learning and Computer ScienceOne of the energies that can be utilized from the high intensity of sunlight in Indonesia is by maximizing the device for converting sunlight into electrical energy called solar panels. The amount of output power produced by solar panels is influenced by several environmental conditions where a solar panel is placed, such as temperature, intensity of sunlight, direction of sunlight and the spectrum of sunlight. Environmental conditions are always changing all the time causing the output power of solar panels to also fluctuate. Monitoring the output parameters of solar panels is very necessary to assess the performance of a solar panel when changing the intensity of sunlight. Monitoring using software aims to ensure real-time monitoring so that monitoring does not require manual methods using measuring instruments in general. The aim of this research is to create an IoT (Internet of Things) based electric current monitoring system on solar panels in the UIN SUSKA Riau Solar Power Plant (PLTS) laboratory. The results of the research carried out show that sending data from the NodeMCU which has been connected to the ACS712 and DHT22 sensors using the blynk application which is carried out for 6 hours is able to detect current, temperature, humidity and power which is displayed well, monitoring can be used using the internet network and the blynk application . This blynk application can be accessed via Android or by using the website so that it can be used more efficiently over short or long distances.
This research has successfully developed an IoT-based electric current monitoring system for solar panels in the PLTS laboratory of UIN SUSKA Riau.The system is capable of detecting and displaying current, temperature, humidity, and power effectively through the Blynk application.The monitoring system can be accessed remotely via Android or a website, offering convenience for both short and long-distance monitoring.
Further research could explore the integration of machine learning algorithms to predict solar panel performance based on historical data and environmental factors, enabling proactive maintenance and optimization of energy generation. Additionally, investigating the use of alternative wireless communication protocols beyond Blynk, such as LoRaWAN or Sigfox, could extend the systems range and reduce power consumption for deployment in remote areas. Finally, a study on the economic feasibility of implementing this monitoring system on a larger scale, considering the cost of sensors, data transmission, and potential energy savings, would be valuable for wider adoption and contribute to the development of sustainable energy solutions. These investigations will enhance the reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of solar energy monitoring systems, ultimately promoting the broader utilization of renewable energy sources.
- http://jurnal.usbypkp.ac.id/index.php/infotronik. penerapan internet things sistem monitoring irigasi... doi.org/10.32897/infotronik.2018.3.2.108jurnal usbypkp ac index php infotronik penerapan internet things sistem monitoring irigasi doi 10 32897 infotronik 2018 3 2 108
- Sistem Monitoring berbasis Internet of things pada Suhu dan Kelembaban Udara di Laboratorium Kimia XYZ... jurnal.politeknik-kebumen.ac.id/index.php/E-KOMTEK/article/view/404Sistem Monitoring berbasis Internet of things pada Suhu dan Kelembaban Udara di Laboratorium Kimia XYZ jurnal politeknik kebumen ac index php E KOMTEK article view 404
- Analisa Pengembangan Sistem Pemantau Daya Listrik Berbasis IoT | Jurnal Teknik. analisa pengembangan... jt.ft.ung.ac.id/index.php/jt/article/view/185Analisa Pengembangan Sistem Pemantau Daya Listrik Berbasis IoT Jurnal Teknik analisa pengembangan jt ft ung ac index php jt article view 185
| File size | 394.92 KB |
| Pages | 7 |
| DMCA | ReportReport |
Related /
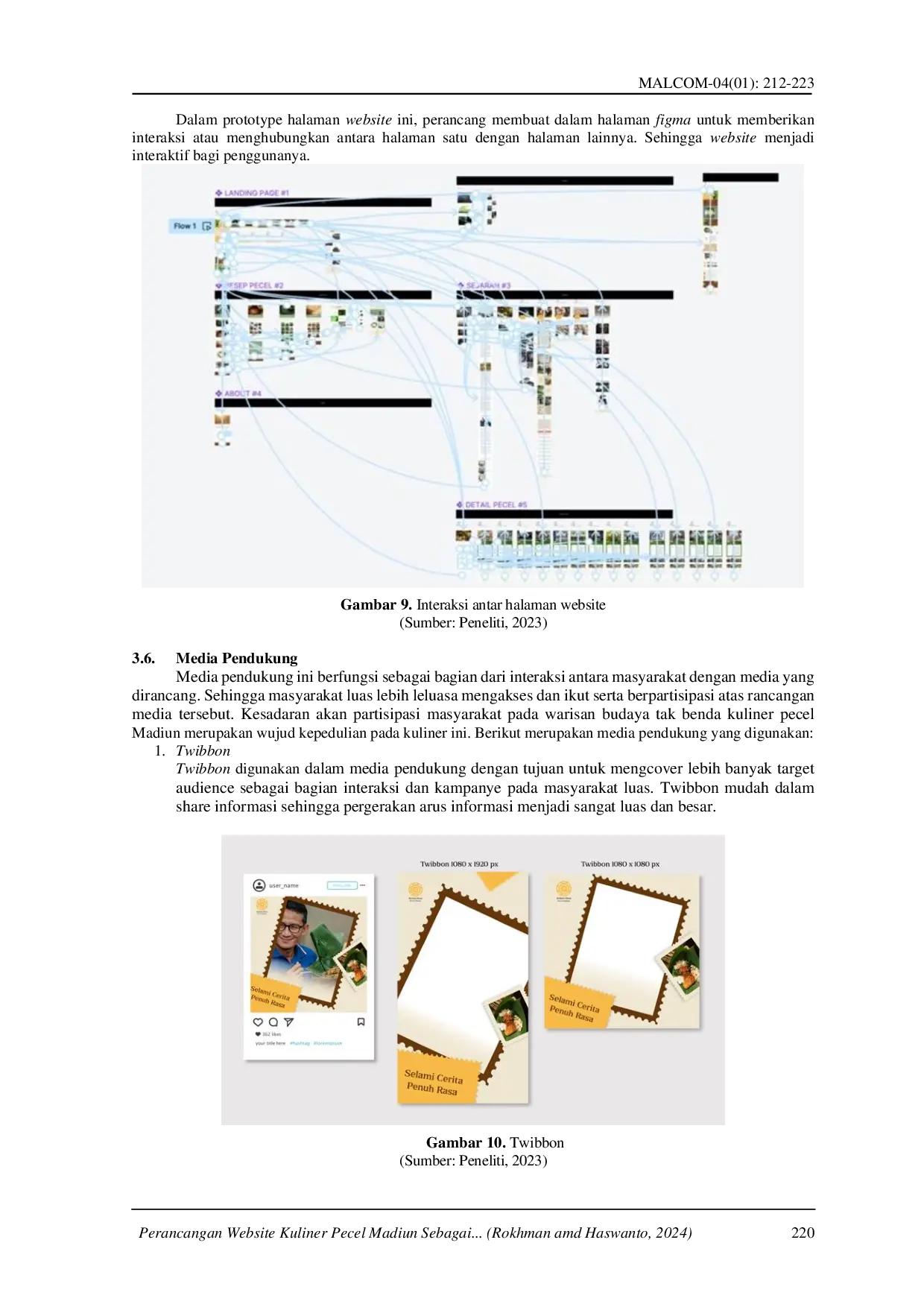
IRPIIRPI Melalui bentuk, gaya serta pola komunikasi visual yang ingin diwujudkan dalam website warisan budaya kuliner pecel Madiun. Tujuan utama perancangan iniMelalui bentuk, gaya serta pola komunikasi visual yang ingin diwujudkan dalam website warisan budaya kuliner pecel Madiun. Tujuan utama perancangan ini
IRPIIRPI Purwarupa telah berhasil dibangun dan dapat mengamatai keadaan lingkungan sekitar alat dengan baik, berdasarkan beberapa kali percobaan pembacaan dataPurwarupa telah berhasil dibangun dan dapat mengamatai keadaan lingkungan sekitar alat dengan baik, berdasarkan beberapa kali percobaan pembacaan data
IRPIIRPI Bank BPD XYZ telah memiliki 144 aplikasi yang dikelola secara mandiri di Data Center dan Disaster Recovery Center Bank BPD XYZ. Berdasarkan laporan monitoringBank BPD XYZ telah memiliki 144 aplikasi yang dikelola secara mandiri di Data Center dan Disaster Recovery Center Bank BPD XYZ. Berdasarkan laporan monitoring
IRPIIRPI Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk membuat video profil Universitas Muhammadiyah Kendari yang dikemas dalam bentuk video. Penelitian ini merupakan penelitianPenelitian ini bertujuan untuk membuat video profil Universitas Muhammadiyah Kendari yang dikemas dalam bentuk video. Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian
Useful /
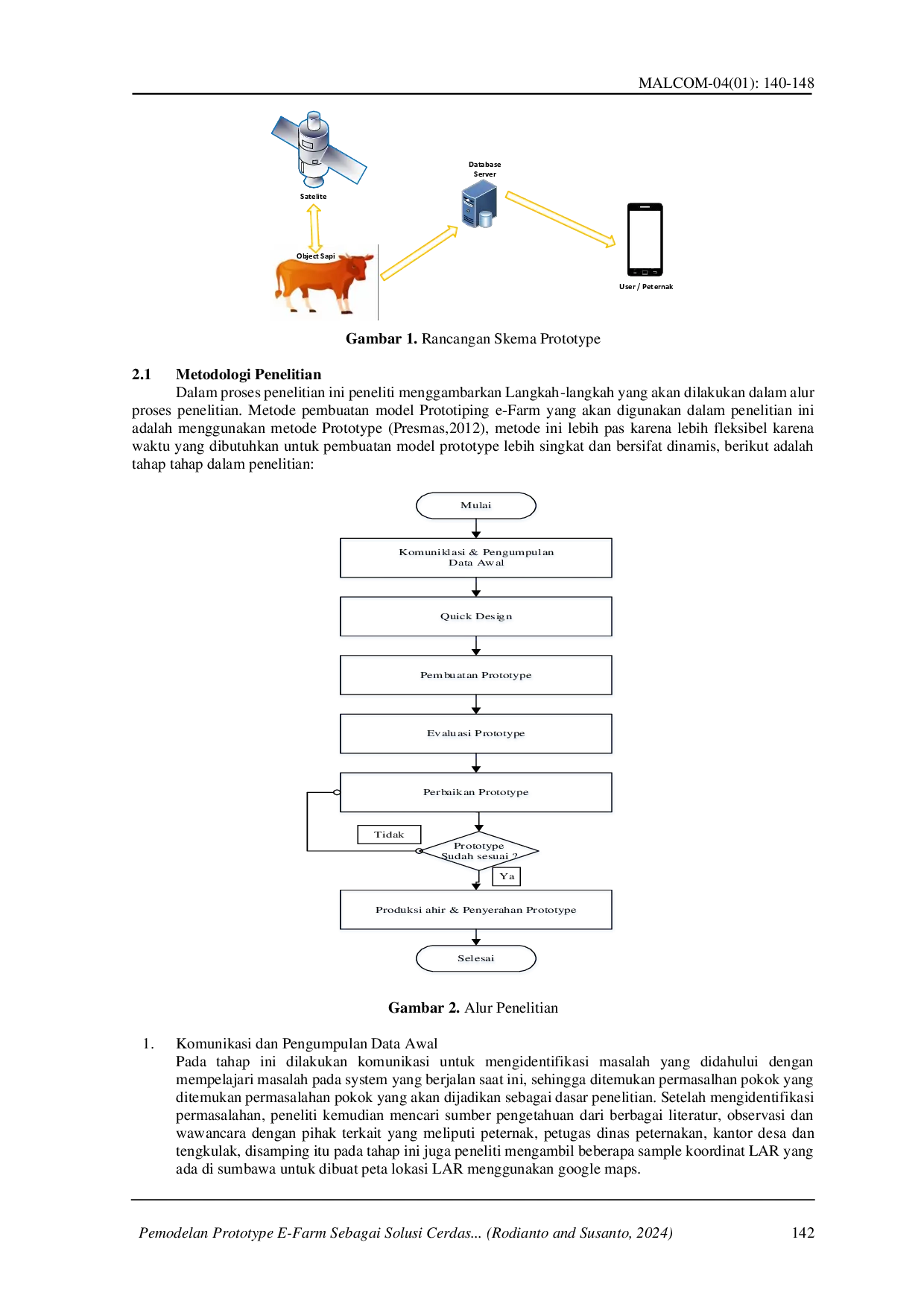
IRPIIRPI Potensi sektor peternakan, khususnya di Pulau Sumbawa, menjadi sentra utama pengembangan ternak sapi untuk mendukung program NTB Bumi Sejuta Sapi (NTB-BSS)Potensi sektor peternakan, khususnya di Pulau Sumbawa, menjadi sentra utama pengembangan ternak sapi untuk mendukung program NTB Bumi Sejuta Sapi (NTB-BSS)
IRPIIRPI Telepon seluler merupakan perangkat yang sering digunakan untuk pembelajaran online pada masa pandemik covid-19. Banyak pilihan dengan beragam spesifikasiTelepon seluler merupakan perangkat yang sering digunakan untuk pembelajaran online pada masa pandemik covid-19. Banyak pilihan dengan beragam spesifikasi
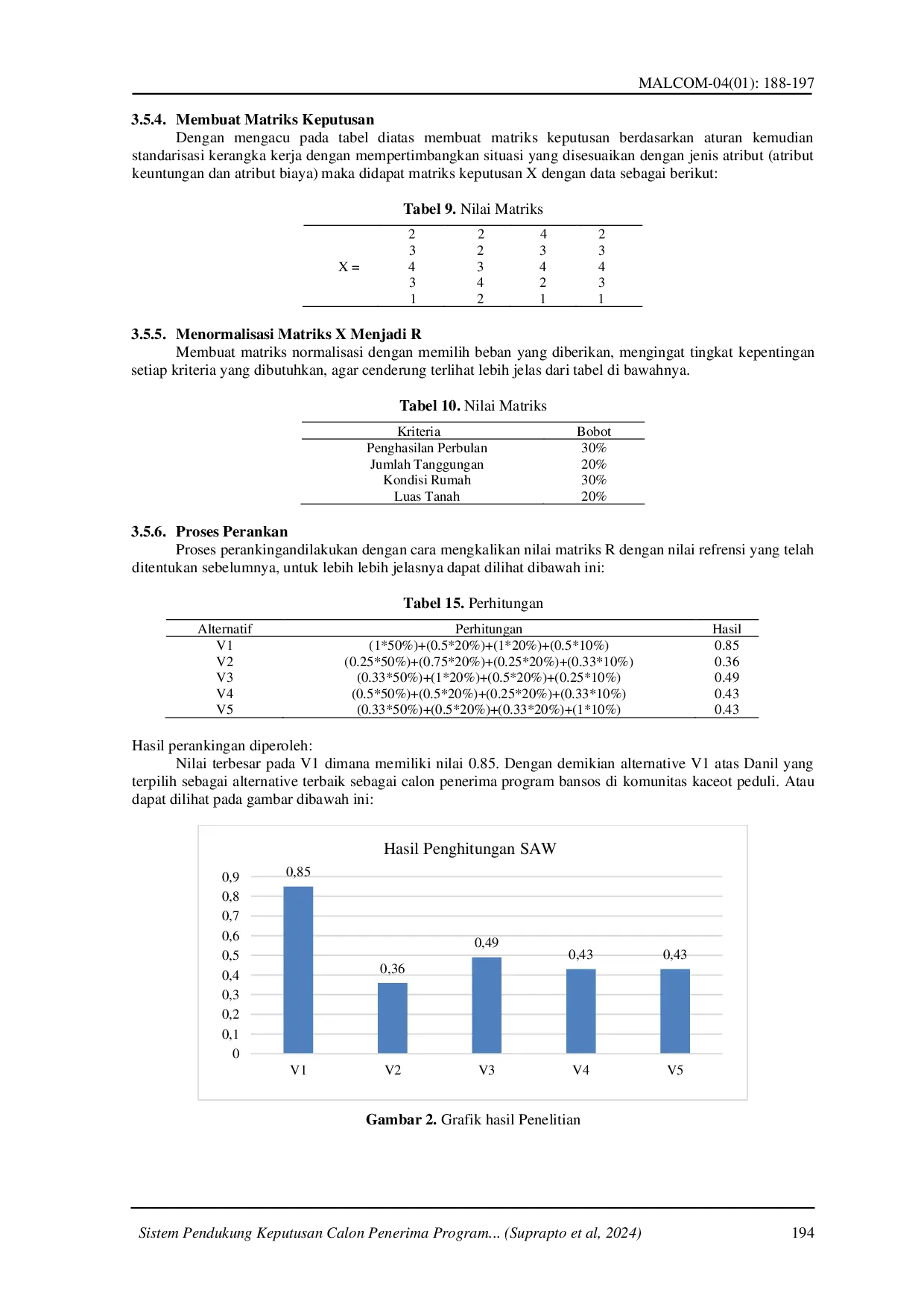
IRPIIRPI Proses identifikasi penerima program bantuan sosial di Kp Kaceot Peduli 2 Kerawang barat relatif memakan waktu dan kurang optimal, karena merupakan prosesProses identifikasi penerima program bantuan sosial di Kp Kaceot Peduli 2 Kerawang barat relatif memakan waktu dan kurang optimal, karena merupakan proses
IRPIIRPI Meningkatnya kasus stunting pada balita memerlukan suatu upaya dalam penanganan dan pencegahan secara dini. Terdapat 17 atribut pada data stunting yangMeningkatnya kasus stunting pada balita memerlukan suatu upaya dalam penanganan dan pencegahan secara dini. Terdapat 17 atribut pada data stunting yang